Unit 7: Transformations
7.0 What is Transformation?
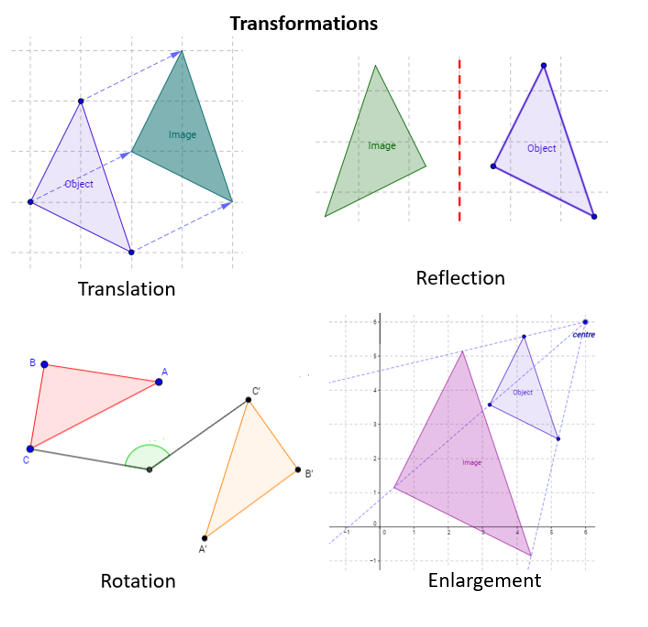
A transformation is a change in the position, orientation, or size of a geometric object.
The original object is called the object.
The result of the transformation is called the image.
Types of Transformation:
Isometric Transformation: Object and image are congruent (same size and shape).
Examples: Reflection, Rotation, Translation
Non-Isometric Transformation: Object and image are similar (shape same, size changes).
Example: Enlargement
7.1 Reflection
Definition:
A reflection is a transformation where a figure is flipped across a line called the axis of reflection. The perpendicular distance from the line to each point of the object and its image is equal.
Properties:
Points on the mirror line are invariant.
Reflection preserves lengths and angles (congruent).
Object and image are mirror-reverse of each other.
Lines perpendicular to the mirror line are invariant, but points on them are not.
Examples in Daily Life:
Mirror reflection of your face.
Reflection in calm water.
Rearview mirrors in vehicles.
Reflection in Cartesian Plane
Axis / LineImage of P(x, y)x-axis (y=0)(x, –y)y-axis (x=0)(–x, y)y = x(y, x)y = –x(–y, –x)x = a(2a – x, y)y = b(x, 2b – y)
Examples:
Point (4, –2) reflected in x-axis → (4, 2)
Point (3, 1) reflected in y = –x → (–1, –3)
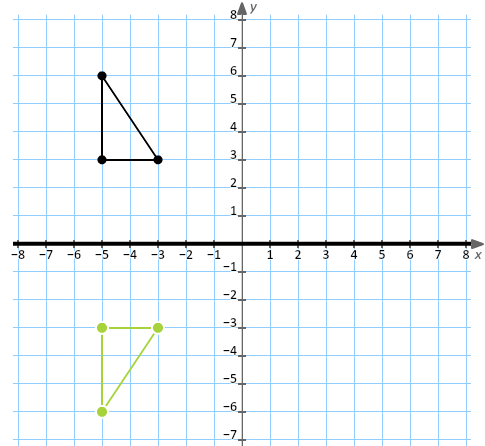
7.2 Rotation
Definition:
A rotation moves a figure around a fixed point called the centre of rotation by a certain angle of rotation. Each point remains at a constant distance (radius) from the center.
Properties:
Centre of rotation is invariant.
Distances from the centre are preserved.
Object and image are congruent.
Perpendicular bisector of the segment joining a point and its image passes through the centre.
Rotation about the Origin (0,0)
Fig2 : Table
Rotation about a Point (a,b)
Fig3 : Table
Examples:
Point (–2, 4) rotated –90° about origin → (4, 2)
Point (1, –3) rotated 270° about origin → (–3, –1)
Fig 1
7.3 Translation
Definition:
Translation moves every point of an object by the same distance and direction, defined by a vector.
Properties:
Object and image are congruent.
Each point moves equally along the vector.
Translation is a direct isometric transformation.
Translation in Cartesian Plane
Definition:
Slide a figure along a vector.
Properties:
Object and image are congruent.
Each point moves the same distance in the same direction.
Translation Rule:
If a point is P(x,y)P(x, y)P(x,y) and the translation vector is T⃗=(a,b)\vec{T} = (a, b)T=(a,b), then:
P(x,y)→P′(x+a,y+b)P(x, y) \to P'(x + a, y + b)P(x,y)→P′(x+a,y+b)
Examples:
Point (2, 3) translated by T⃗=(4,0)\vec{T} = (4, 0)T=(4,0):
P′(2,3)=(2+4,3+0)=(6,3)P'(2, 3) = (2 + 4, 3 + 0) = (6, 3)P′(2,3)=(2+4,3+0)=(6,3)
Point (3, –4) translated by T⃗=(−4,3)\vec{T} = (-4, 3)T=(−4,3):
P′(3,−4)=(3−4,−4+3)=(−1,−1)P'(3, -4) = (3 - 4, -4 + 3) = (-1, -1)P′(3,−4)=(3−4,−4+3)=(−1,−1)

7.4 Enlargement (Scaling)
Definition:
Enlargement is a transformation that changes the size of a figure but keeps the shape same. The fixed point is called the centre of enlargement.
Scale factor > 1 → Enlargement (bigger)
Scale factor < 1 → Reduction (smaller)
Formula:
If the centre of enlargement is O(0,0) and scale factor k, then
Image of P(x, y) → P'(kx, ky)
Coordinates Quick Reference
Reflection:
x-axis → (x, –y)
y-axis → (–x, y)
y = x → (y, x)
y = –x → (–y, –x)
Rotation about origin:
+90° → (–y, x)
+180° → (–x, –y)
+270° → (y, –x)
Translation:
Vector (a, b) → (x + a, y + b)
Enlargement:
Scale k → (kx, ky)
Important Questions
Q1: Reflect the points A(3,5) and B(–2,–1) in the x-axis and y-axis.
Solution:
, Step 1: Reflection in x-axis:
A(3,5) → (3, –5)
B(–2,–1) → (–2, 1)
, Step 2: Reflection in y-axis:
A(3,5) → (–3, 5)
B(–2,–1) → (2, –1)
Q2: Rotate P(4,2) and Q(–3,–2) through 90° about the origin.
Solution:
, Step 1: Use rotation formula for +90°: (x, y) → (–y, x)
P(4,2) → (–2, 4)
Q(–3,–2) → (2, –3)
Q3: Translate R(2,3) by vector (4,0) and S(–1,–2) by vector (–2,3).
Solution:
, Step 1: Translation formula: P(x, y) → (x + a, y + b)
R(2,3) by (4,0) → (2+4, 3+0) → (6,3)
, Step 2: S(–1,–2) by (–2,3) → (–1–2, –2+3) → (–3,1)
Q4: Find the image of P(2,3) under enlargement with centre O(0,0) and scale factor 2.
Solution:
, Step 1: Use enlargement formula: P(x, y) → (kx, ky)
, Step 2: P(2,3) → (2×2, 2×3) → (4,6)
Q5: Reflect P(3,4) in y = x, then rotate the image 180° about origin.
Solution:
, Step 1: Reflection in y = x: P(3,4) → (4,3)
, Step 2: Rotation 180° about origin: (x, y) → (–x, –y)
(4,3) → (–4, –3)
Q6: Translate A(–2,5) by vector (3,–7), then reflect the image in x-axis.
Solution:
, Step 1: Translation: A(–2,5) → (–2+3, 5–7) → (1,–2)
, Step 2: Reflection in x-axis: (1,–2) → (1,2)
Q7: Rotate B(–1,2) 270° about origin, then enlarge with scale factor 3.
Solution:
, Step 1: Rotation 270°: (x, y) → (y, –x)
B(–1,2) → (2,1)
, Step 2: Enlargement with scale factor 3: (2,1) → (6,3)
For further practice visit this link !!
https://besidedegree.com/exam/s/academic
Gallery
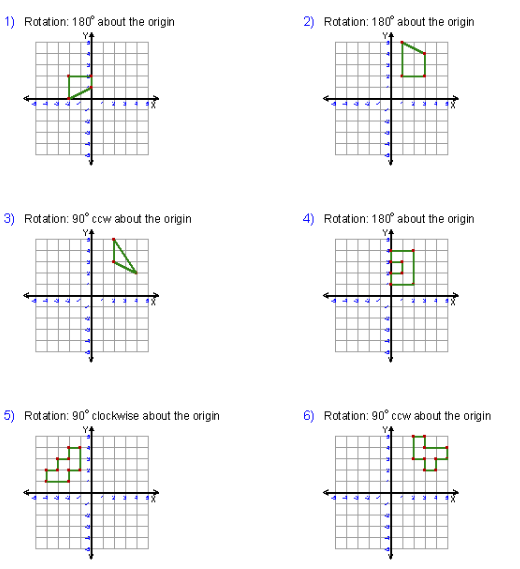
Fig 1

Fig 2:Rotation About the Origin (0,0)