17.1 Introduction to Trigonometry
Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the relationship between angles and sides of a triangle, especially a right-angled triangle.
It is used to find heights and distances of objects which cannot be measured directly, such as trees, buildings, towers, poles, rivers, etc.
Trigonometry is widely used in mathematics, physics, engineering, astronomy, and navigation.
Right Angled Triangle Terms
In a right-angled triangle:
• Right angle = 90°
• Reference angle (θ) = acute angle used for trigonometric ratios
With respect to reference angle θ:
Hypotenuse (h) → longest side (opposite to 90°)
Perpendicular (p) → side opposite to θ
Base / Adjacent (b) → side adjacent to θ
17.1.2 Fundamental Trigonometric Ratios
In a right-angled triangle:
• Sine of θ
sinθ = Perpendicular / Hypotenuse
sinθ = p / h
• Cosine of θ
cosθ = Base / Hypotenuse
cosθ = b / h
• Tangent of θ
tanθ = Perpendicular / Base
tanθ = p / b
These three are called basic trigonometric ratios.
Other Trigonometric Ratios
• Cosecant
cosecθ = 1 / sinθ = h / p
• Secant
secθ = 1 / cosθ = h / b
• Cotangent
cotθ = 1 / tanθ = b / p
Important Identity
sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
This identity is true for all angles θ.
Effect of Triangle Size
The size of the triangle does not affect trigonometric ratios.
Only the angle θ matters.
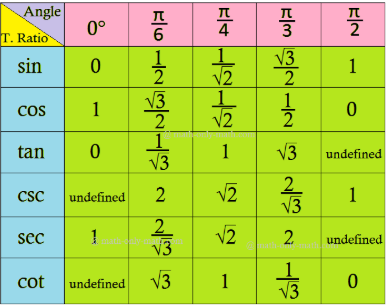
17.2 Trigonometric Ratios of Some Special Angles
Special Angles
0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°
Values of Trigonometric Ratios
Fig [1]
Complementary Angle Relations
sin(90° − θ) = cosθ
cos(90° − θ) = sinθ
Solved Examples
Example 1
Find height of a pole if hypotenuse = 10 m and base = 8 m.
or, h = 10 m
or, b = 8 m
Using Pythagoras theorem:
or, h² = p² + b²
or, 10² = p² + 8²
or, 100 = p² + 64
or, p² = 36
or, p = 6
Height of the pole = 6 m
Example 2
If sinθ = 3/5 and h = 20, find p.
or, sinθ = p / h
or, 3/5 = p / 20
or, 5p = 3 × 20
or, p = 12
Example 3
If cosθ = 4/5 and b = 8, find h.
or, cosθ = b / h
or, 4/5 = 8 / h
or, 4h = 40
or, h = 10
Example 4
Express tanθ in terms of cosθ.
or, tanθ = p / b
or, p = √(h² − b²)
or, tanθ = √(1 − cos²θ) / cosθ
10 Important Exam Questions (Solved)
1. If tanθ = 3/4, find sinθ and cosθ.
or, tanθ = p / b = 3 / 4
or, p = 3, b = 4
Using Pythagoras theorem:
or, h² = 3² + 4²
or, h = 5
or, sinθ = 3 / 5
or, cosθ = 4 / 5
2. If sinθ = 5/13, find cosθ and tanθ.
or, p = 5, h = 13
or, b² = 13² − 5²
or, b = 12
or, cosθ = 12 / 13
or, tanθ = 5 / 12
3. Prove sin²θ + cos²θ = 1.
or, sinθ = p / h
or, cosθ = b / h
or, sin²θ + cos²θ = (p² + b²) / h²
or, = h² / h²
or, = 1
4. Find tan60°.
or, tan60° = √3
5. Find sin45°.
or, sin45° = 1 / √2
6. If h = 5 cm and θ = 30°, find p and b.
or, sin30° = p / h
or, 1/2 = p / 5
or, p = 2.5
or, cos30° = b / h
or, √3/2 = b / 5
or, b = (5√3)/2
7. Evaluate sin0° + cos0°.
or, sin0° = 0
or, cos0° = 1
or, sum = 1
8. If cosθ = 1/2, find θ.
or, cos60° = 1/2
or, θ = 60°
9. Evaluate tan45° + sin30°.
or, tan45° = 1
or, sin30° = 1/2
or, sum = 3/2
10. If sinθ = 6/10 and h = 20, find b.
or, p / h = 6 / 10
or, p = 12
or, b² = 20² − 12²
or, b² = 256
or, b = 16
For further practice visit this link !!
https://besidedegree.com/exam/s/academic
Gallery