TRIGONOMETRY – UNIT 5 (COMPLETE NOTES)
5.0 INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY
Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the relationship between angles and sides of a triangle, especially a right-angled triangle.
In a right-angled triangle:
One angle is 90°
The side opposite 90° is called the Hypotenuse (h)
The side opposite the reference angle is called Perpendicular (p)
The remaining side is called Base (b)
5.1 MEASUREMENT OF ANGLES
Definition of Angle
An angle is the amount of rotation of a line about a fixed point.
Anti–clockwise rotation → Positive angle (+θ)
Clockwise rotation → Negative angle (−θ)
SYSTEMS OF MEASURING ANGLES
There are three systems of measuring angles:
Sexagesimal System (Degree measure)
Centesimal System (Grade measure)
Circular System (Radian measure)
(i) SEXAGESIMAL SYSTEM (DEGREE MEASURE)
Right angle = 90°
1° = 60 minutes (')
1' = 60 seconds (")
Important Relations
1 right angle = 90° = 5400' = 324000"
Conversion Formulas
Degrees to minutes: 1° = 60'
Degrees to seconds: 1° = 3600"
(ii) CENTESIMAL SYSTEM (GRADE MEASURE)
Right angle = 100g
1g = 100 minutes (')
1' = 100 seconds (")
Important Relations
1 right angle = 100g = 10000' = 1000000"
(iii) CIRCULAR SYSTEM (RADIAN MEASURE)
Definition of Radian
An angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius is called 1 radian.
Important Facts
180° = π radian
90° = π/2 radian
1 radian = 180°/π
Formula
θ (in radian) = Arc length (l) / Radius (r)
RELATION BETWEEN DEGREE, GRADE AND RADIAN
90° = 100g = π/2 radian
1° = (10/9) g
1° = π/180 radian
1g = (9/10)°
1g = π/200 radian
IMPORTANT FIGURES (DIAGRAMS)
FIGURE 1: RIGHT ANGLED TRIANGLE (BASIC TRIGONOMETRY)
Angle at B = θ
Hypotenuse (h): Side opposite 90°
Perpendicular (p): Side opposite angle θ
Base (b): Side adjacent to angle θ
This figure is used to define all six trigonometric ratios.
FIGURE 2: UNIT CIRCLE FOR RADIAN MEASURE
Center = O
Radius = r
Arc length = l
Angle in radian: θ = l / r
Used to understand radian measure and conversion.
FIGURE 3: STANDARD ANGLES (30°, 45°, 60°)
(a) 30°–60°–90° Triangle
Ratios:
sin 30° = 1/2
cos 30° = √3/2
tan 30° = 1/√3
(b) 45°–45°–90° Triangle
Ratios:
sin 45° = 1/√2
cos 45° = 1/√2
tan 45° = 1
FIGURE 4: QUADRANTS AND SIGNS OF TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS
Mnemonic: ASTC Rule
Quadrant I: All ratios +ve
Quadrant II: Sin +ve
Quadrant III: Tan +ve
Quadrant IV: Cos +ve
5.2 TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS
Trigonometric Ratios in Right Angled Triangle
Let θ be the reference angle:
sin θ = p / h
cos θ = b / h
tan θ = p / b
cot θ = b / p
sec θ = h / b
cosec θ = h / p
RECIPROCAL RELATIONS
sin θ × cosec θ = 1
cos θ × sec θ = 1
tan θ × cot θ = 1
QUOTIENT RELATIONS
tan θ = sin θ / cos θ
cot θ = cos θ / sin θ
PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES
sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
sec²θ − tan²θ = 1
cosec²θ − cot²θ = 1
5.3 TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS OF STANDARD ANGLES
Values of Trigonometric Ratios
5.4 IMPORTANT THEOREMS IN TRIGONOMETRY
THEOREM 1: PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITY
Statement:
In a right-angled triangle,
sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
Proof:
Let the perpendicular = p, base = b and hypotenuse = h
sin θ = p/h and cos θ = b/h
sin²θ + cos²θ
= p²/h² + b²/h²
= (p² + b²)/h²
Using Pythagoras theorem:
p² + b² = h²
So,
= h²/h²
= 1
Hence proved.
THEOREM 2: SECOND PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITY
Statement:
1 + tan²θ = sec²θ
Proof:
We know:
tan θ = p/b and sec θ = h/b
LHS = 1 + tan²θ
= 1 + p²/b²
= (b² + p²)/b²
Using Pythagoras theorem:
= h²/b²
= (h/b)²
= sec²θ
Hence proved.
THEOREM 3: THIRD PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITY
Statement:
1 + cot²θ = cosec²θ
Proof:
We know:
cot θ = b/p and cosec θ = h/p
LHS = 1 + cot²θ
= 1 + b²/p²
= (p² + b²)/p²
Using Pythagoras theorem:
= h²/p²
= (h/p)²
= cosec²θ
Hence proved.
5.5 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES
A trigonometric identity is an equation that is true for all values of the angle.
Common Identities
1 + tan²θ = sec²θ
1 + cot²θ = cosec²θ
1 − sin²θ = cos²θ
1 − cos²θ = sin²θ
5.5 TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS OF ANY ANGLE
Signs of Trigonometric Ratios in Quadrants

IMPORTANT QUESTIONS WITH SOLUTIONS
Q1. Convert 30° into radian
Solution:
30° = 30 × π/180
= π/6 radian
Q2. If sin θ = 3/5, find cos θ and tan θ
Step 1: sin θ = p/h = 3/5
Let p = 3, h = 5
Step 2: Using Pythagoras theorem
b² = h² − p²
b² = 25 − 9 = 16
b = 4
Step 3: Find required ratios
cos θ = b/h = 4/5
tan θ = p/b = 3/4
Q3. Find the value of (sin 60° + cos 30°) tan 30°
Step 1: Write values
sin 60° = √3/2
cos 30° = √3/2
tan 30° = 1/√3
Step 2: Substitute
= (√3/2 + √3/2) × 1/√3
= √3 × 1/√3
= 1
Q4. Prove: sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
Proof:
In right triangle:
sin θ = p/h, cos θ = b/h
sin²θ + cos²θ = p²/h² + b²/h²
= (p² + b²)/h²
= h²/h² = 1
Hence proved.
Q5. Find the third angle of a right-angled triangle if one angle is 30° (in grade)
Step 1: Convert 30° into grade
30° = 30 × 10/9 = 33.33g
Step 2: Sum of angles in triangle = 200g
Third angle = 200g − (100g + 33.33g)
= 66.67g
MORE IMPORTANT QUESTIONS WITH SOLUTIONS
Q6. If cos θ = 5/13, find all other trigonometric ratios
Step 1:
cos θ = b/h = 5/13
Let b = 5, h = 13
Step 2: Find perpendicular using Pythagoras theorem
p² = h² − b²
p² = 169 − 25 = 144
p = 12
Step 3: Find remaining ratios
sin θ = p/h = 12/13
tan θ = p/b = 12/5
cot θ = b/p = 5/12
sec θ = h/b = 13/5
cosec θ = h/p = 13/12
Q7. Evaluate: (sin 30° cos 60° + cos 30° sin 60°)
Step 1: Use identity
sin A cos B + cos A sin B = sin (A + B)
Step 2: Substitute values
= sin (30° + 60°)
= sin 90°
= 1
Q8. Prove: (1 + tan²θ) / (1 + sec²θ) = sin²θ
Proof:
LHS = (1 + tan²θ) / (1 + sec²θ)
Using identities:
1 + tan²θ = sec²θ
1 + sec²θ = 1 + sec²θ
LHS = sec²θ / (1 + sec²θ)
Divide numerator and denominator by sec²θ
= 1 / (1/sec²θ + 1)
= 1 / (cos²θ + 1)
= sin²θ
Hence proved.
Q9. Find the value of tan 45° + 2 sin 30°
Step 1: Write values
tan 45° = 1
sin 30° = 1/2
Step 2: Substitute
= 1 + 2 × 1/2
= 1 + 1
= 2
Q10. Convert π/3 radian into degree
Step 1: Use relation
180° = π radian
Step 2: Convert
π/3 = (π/3) × 180°/π
= 60°
Q11. If tan θ = 1, find the value of sin θ + cos θ
Step 1:
tan θ = 1 = p/b
So p = b
Step 2: Assume p = b = 1
h = √(1² + 1²) = √2
Step 3: Find sin θ + cos θ
= p/h + b/h
= 1/√2 + 1/√2
= √2
Q12. Prove: cosec θ (1 − sin²θ) = sin θ sec θ
Proof:
LHS = cosec θ (1 − sin²θ)
= (1/sin θ) × cos²θ
= cos²θ / sin θ
= cos θ × (cos θ / sin θ)
= cos θ × cot θ
= sin θ sec θ
Hence proved.
Q13.One angle of a right-angled triangle is 27°. Find its third angle in grade measure.(Fig 5)
Solution In a right-angled triangle ABC, ∠B = 100ᵍ,
∠C = 27° = 27 × (10/9)ᵍ = 30ᵍ, ∠A = ?
Now, we know that ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 200ᵍ [ ∵ Sum of interior angles of triangle in grade ]
or, ∠A + 100ᵍ + 30ᵍ = 200ᵍ
or, ∠A = 200ᵍ – 130ᵍ = 70ᵍ
∴ The required third angle of the triangle is 70ᵍ.
For further practice visit this link !!
https://besidedegree.com/exam/s/academic
Gallery
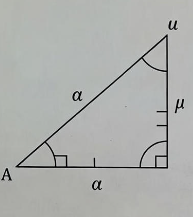
Fig 1
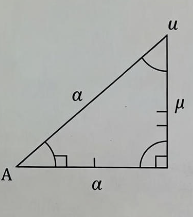
Fig 2
Fig 3