1. INTRODUCTION TO VECTORS
A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Examples: Velocity, Displacement, Force, Acceleration
A scalar has only magnitude, no direction.
Examples: Distance, Speed, Mass, Time
2. REPRESENTATION OF A VECTOR
A vector is represented by a directed line segment.
Length of the line shows magnitude
Arrow shows direction
Notation:
Vector from point A to B: AB
Magnitude of vector AB: |AB|
Figure 1: Vector Representation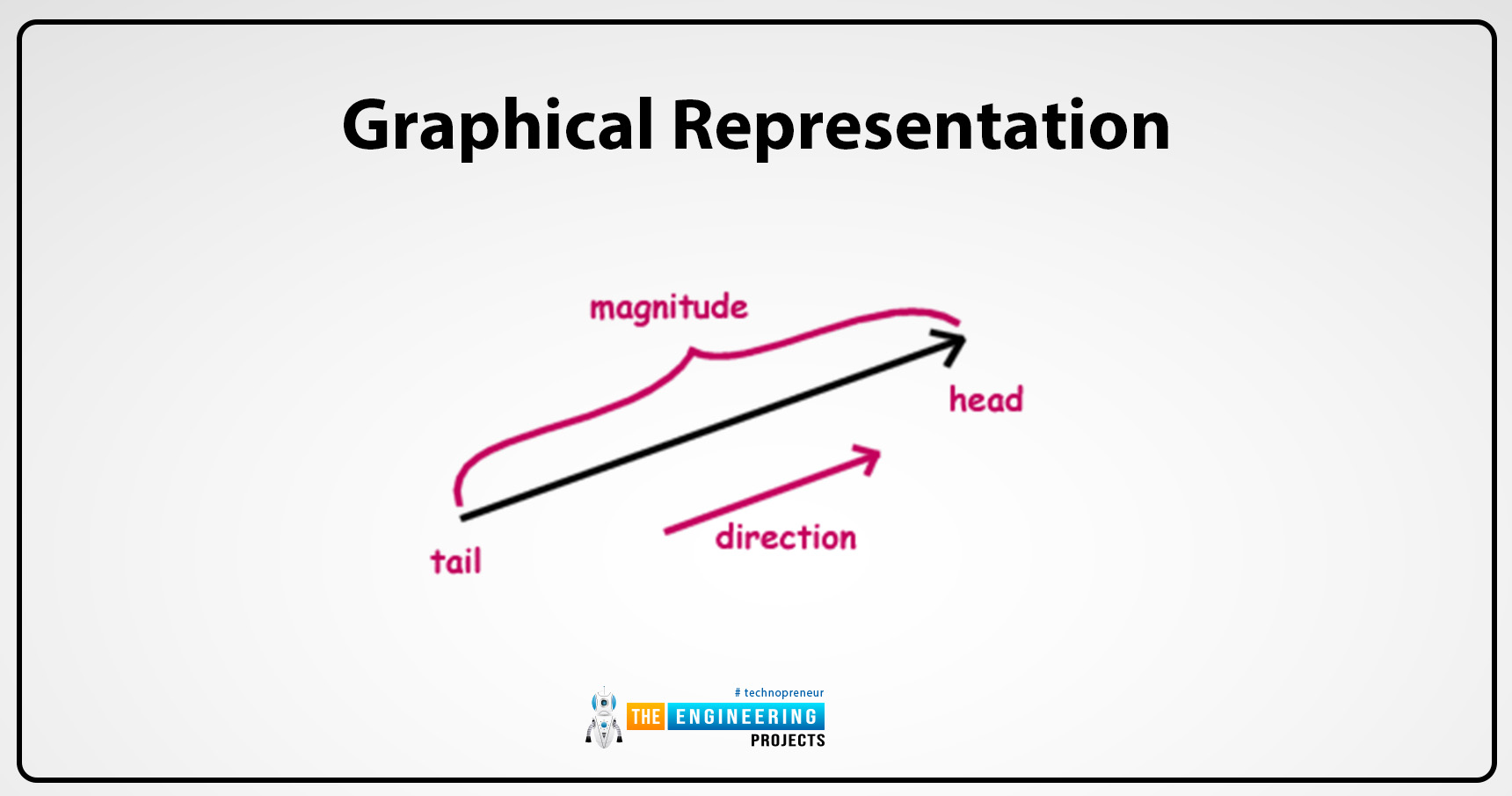
A = Initial point
B = Terminal point
Vector = AB
Magnitude = Length of AB
3. TYPES OF VECTORS
Zero Vector: Magnitude = 0, no definite direction
Unit Vector: Magnitude = 1, shows only direction
Equal Vectors: Same magnitude, same direction
Negative Vectors: Same magnitude, opposite direction
Figure 2: Equal and Negative Vectors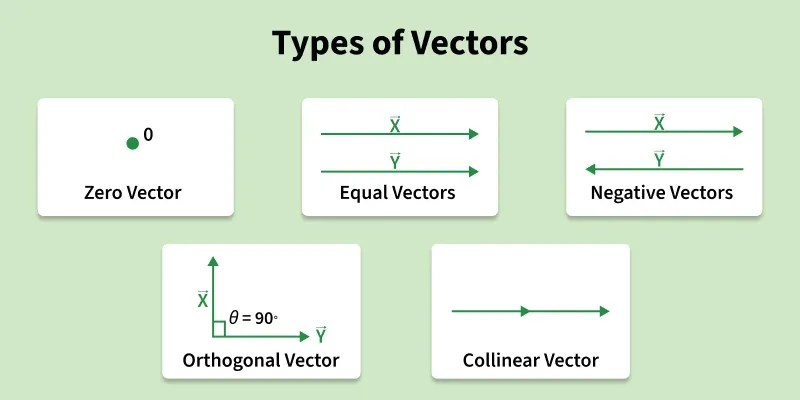
4. ADDITION OF VECTORS
Vector addition finds a single vector equivalent to two or more vectors.
Methods:
Triangle Law
Parallelogram Law
5. TRIANGLE LAW OF VECTOR ADDITION
Statement: If two vectors are represented by two sides of a triangle taken in order, the third side taken in opposite order represents the resultant.
Figure 3: Triangle Law
AB = First vector
BC = Second vector
AC = Resultant vector
6. PARALLELOGRAM LAW OF VECTOR ADDITION
Statement: If two vectors act at a point and are represented by adjacent sides of a parallelogram, then the diagonal passing through that point represents the resultant vector.
Figure 4: Parallelogram Law

AB and AD = Vectors
AC = Resultant vector
7. SUBTRACTION OF VECTORS
Vector Subtraction:
A - B = A + (-B)
Subtraction is done by adding the negative vector.
Figure 5: Vector Subtraction
8. MULTIPLICATION OF VECTOR BY A SCALAR
Multiply vector by real number: scalar multiplication
If k > 0 → same direction
If k < 0 → opposite direction
9. POSITION VECTOR
A vector that represents the position of a point relative to the origin.
If O = origin and A = point, then OA = position vector of A
Figure 6: Position Vector
10. IMPORTANT NUMERICAL QUESTIONS (WITH STEPWISE SOLUTIONS)
Q1. If AB = 5i + 2j and BC = i - j, find AC.
Solution:
Step 1: AC = AB + BC
Step 2: AC = (5i + 2j) + (i - j)
Step 3: AC = (5 + 1)i + (2 - 1)j = 6i + 1j
Answer: AC = 6i + j
Q2. If a = 3i + 4j, find |a|.
Solution:
|a| = sqrt((3)^2 + (4)^2) = sqrt(9 + 16) = sqrt(25) = 5
Answer: |a| = 5
Q3. Find the negative of a = 2i - 3j.
Solution:
-a = -(2i - 3j) = -2i + 3j
Answer: -a = -2i + 3j
Q4. If vector a = 4i + 2j, find 3a.
Solution:
3a = 3*(4i + 2j) = 12i + 6j
Answer: 3a = 12i + 6j
Q5. Find the resultant of vectors AB = 2i + 3j and AC = -i + 4j.
Solution:
R = AB + AC = (2i + 3j) + (-i + 4j) = i + 7j
Answer: R = i + 7j
Q6. Find |R| for R = 3i - 4j.
Solution:
|R| = sqrt(3^2 + (-4)^2) = sqrt(9 + 16) = sqrt(25) = 5
Answer: |R| = 5
Q7. If a = 2i + j, b = i - 2j, find a - b.
Solution:
Step 1: a - b = a + (-b)
Step 2: -b = -i + 2j
Step 3: a - b = (2i + j) + (-i + 2j) = i + 3j
Answer: a - b = i + 3j
Q8. Position vector of point A(2,3) from origin O.
Solution:
OA = xi + yj = 2i + 3j
Answer: OA = 2i + 3j
Q9. If a = 3i + 4j, find unit vector along a.
Solution:
|a| = sqrt(3^2 + 4^2) = 5
â = a / |a| = (3/5)i + (4/5)j
Answer: â = 0.6i + 0.8j
Q10. If AB = 3i + 2j and BC = 2i - j, find AC using triangle law.
Solution:
AC = AB + BC = (3i + 2j) + (2i - j) = 5i + j
Answer: AC = 5i + j
For further practice visit this link !!
https://besidedegree.com/exam/s/academic