- Graph with Points A, B, C, D: Four points forming a quadrilateral (typically on grid).
- Tasks:
- Equation of lines AB, BC, CD, AD: Use two-point form.
- Slopes: m=y2−y1x2−x1m = \frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1}m=x2−x1y2−y1.
- Parallel to x-axis: m = 0.
- Parallel to y-axis: m undefined.
- Slope same in either direction.
- Straight Line Equation:
- Satisfies coordinates on line only.
- Point-slope: y−y1=m(x−x1)y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)y−y1=m(x−x1).
- Two-point: y−y1=y2−y1x2−x1(x−x1)y - y_1 = \frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1}(x - x_1)y−y1=x2−x1y2−y1(x−x1).
4.1 Angle Between Two Straight Lines
- Slope and Inclination: m = tan θ.
- Angle θ Between Lines (slopes m₁, m₂):
- tanθ=∣m1−m21+m1m2∣\tan \theta = \left| \frac{m_1 - m_2}{1 + m_1 m_2} \right|tanθ=1+m1m2m1−m2 (acute angle usually with absolute value; ± for both).
- Acute if numerator/magnitude positive in context; obtuse opposite.
- Parallel: m₁ = m₂ (θ = 0° or 180°).
- Perpendicular: m₁ m₂ = -1.
- General Lines: a₁x + b₁y + c₁ = 0, a₂x + b₂y + c₂ = 0.
- Slopes: m₁ = -a₁/b₁, m₂ = -a₂/b₂.
- tanθ=∣a1b2−a2b1a1a2+b1b2∣\tan \theta = \left| \frac{a_1 b_2 - a_2 b_1}{a_1 a_2 + b_1 b_2} \right|tanθ=a1a2+b1b2a1b2−a2b1.
- Parallel: a₁/a₂ = b₁/b₂ (≠ c₁/c₂).
- Perpendicular: a₁a₂ + b₁b₂ = 0.
- Applications:
- Parallel line through point: Same slope.
- Perpendicular line: Slope = -1/m.
- Lines at given angle (e.g., 60°, 45°): Solve for m using tan formula (two lines).
- Perpendicular bisector: Midpoint + slope = -1/original.
- Diagonals of square: Intersect at midpoint, perpendicular.

4.2 Equation of Pair of Straight Lines
- Homogeneous Second Degree: ax² + 2hxy + by² = 0 (pair through origin).
- Formation: Product of lines y = m₁x, y = m₂x → y² - (m₁ + m₂)xy + m₁ m₂ x² = 0.
- Angle Between Pair:
- tanθ=∣2h2−aba+b∣\tan \theta = \left| \frac{2 \sqrt{h^2 - ab}}{a + b} \right|tanθ=a+b2h2−ab.
- Perpendicular: a + b = 0.
- Parallel/Coincident: h² = ab.
- Separate Lines: Factorize or solve as quadratic in (y/x).
- Combined Equation: Multiply individual lines through origin.
- Perpendicular to Given Pair: Find original slopes, take reciprocals negative, combine.
4.3 Conic Sections
- Right Circular Cone: Vertex O, axis (vertical), generator (slant), base.
- Sections:
- Circle: Plane || base.
- Parabola: Plane || generator.
- Ellipse: Plane angle > vertical angle but <90°.
- Hyperbola: Plane || axis (double cone).


4.4 Circle
- Definition: Locus of point at fixed distance r from centre.
- Equations:
- Centre (0,0): x² + y² = r².
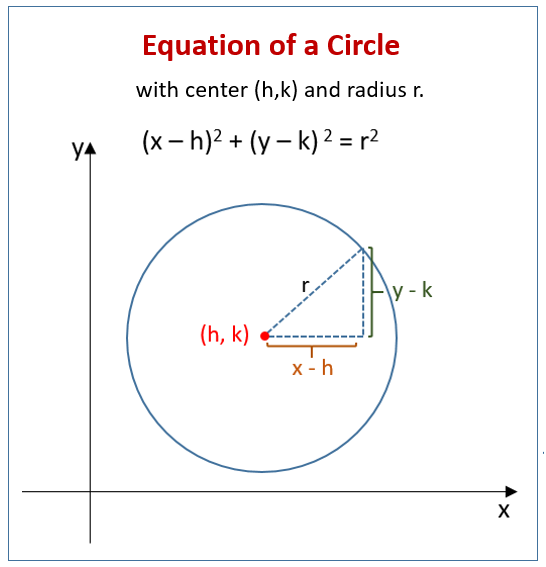
- Centre (h,k): (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r².
- Diameter ends (x₁,y₁), (x₂,y₂): (x - x₁)(x - x₂) + (y - y₁)(y - y₂) = 0.
- General: x² + y² + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 → centre (-g, -f), r = √(g² + f² - c).
- Centre/Radius: Complete square.
- Special:
- Through 3 points: Equidistant centre (solve system).
- Touching axes: Centre (r,r) etc., r = distance to axis.
- Centre on line + through point: Use distance.
- Concyclic: 4 points on one circle.
- Angle in semicircle: 90°.
Question 1
Find the equation of the line passing through (2, 3) and parallel to
4x - 5y + 10 = 0.
Solution:
Given line: 4x - 5y + 10 = 0
Rewrite in slope form:
5y = 4x + 10
y = (4/5)x + 2
So slope m = 4/5
For a parallel line, slope remains same.
Using point-slope form:
y - 3 = (4/5)(x - 2)
Multiply both sides by 5:
5y - 15 = 4x - 8
Rearranging:
4x - 5y + 7 = 0
Question 2
Find the acute angle between the lines
3x - 4y + 5 = 0 and 4x + 3y - 1 = 0.
Solution:
First line:
3x - 4y + 5 = 0
4y = 3x + 5
y = (3/4)x + 5/4
So slope m1 = 3/4
Second line:
4x + 3y - 1 = 0
3y = -4x + 1
y = (-4/3)x + 1/3
So slope m2 = -4/3
Formula for angle between two lines:
tan(theta) = |(m1 - m2) / (1 + m1m2)|
Substitute values:
tan(theta) = |(3/4 + 4/3) / (1 - 1)|
Denominator becomes zero.
Therefore theta = 90 degrees.
So the acute angle between the lines is 90 degrees.
Question 3
Find the combined equation of the pair of lines
x - y = 0 and 2x + y = 0.
Solution:
Combined equation is product of both equations:
(x - y)(2x + y) = 0
Multiply:
2x squared + xy - 2xy - y squared = 0
Simplify:
2x squared - xy - y squared = 0
Question 4
Find the equation of the circle with centre (3, -2) and radius 5.
Solution:
Standard form of circle:
(x - h) squared + (y - k) squared = r squared
Here h = 3, k = -2, r = 5
Substitute:
(x - 3) squared + (y + 2) squared = 25
Expand:
x squared - 6x + 9 + y squared + 4y + 4 = 25
Rearrange:
x squared + y squared - 6x + 4y - 12 = 0
Question 5
Find the centre and radius of the circle
x squared + y squared + 4x - 6y - 12 = 0.
Solution:
Group x and y terms:
(x squared + 4x) + (y squared - 6y) = 12
Complete square:
(x + 2) squared - 4 + (y - 3) squared - 9 = 12
Add constants:
(x + 2) squared + (y - 3) squared = 25
So,
Centre = (-2, 3)
Radius = 5
MORE PRACTICE QUESTIONS (MODERATE TO COMPLEX)
Question 6
Find equation of the line passing through (1, -2) and perpendicular to
2x + 3y - 7 = 0.
Solution:
Given line:
2x + 3y - 7 = 0
3y = -2x + 7
y = (-2/3)x + 7/3
Slope of given line = -2/3
Slope of perpendicular line = 3/2
Using point-slope form:
y + 2 = (3/2)(x - 1)
Multiply by 2:
2y + 4 = 3x - 3
Rearrange:
3x - 2y - 7 = 0
Question 7
Find the angle between lines
x + y = 0 and x - y = 0.
Solution:
First line slope = -1
Second line slope = 1
tan(theta) = |(-1 - 1) / (1 - 1)|
Denominator zero.
So angle = 90 degrees.
Question 8
Find combined equation of pair of lines passing through origin and having slopes 2 and -3.
Solution:
General equation:
(y - 2x)(y + 3x) = 0
Multiply:
y squared + 3xy - 2xy - 6x squared = 0
Simplify:
y squared + xy - 6x squared = 0
Question 9
Find the equation of circle passing through (0,0) with centre on x-axis and radius 5.
Solution:
Let centre be (a, 0).
Using circle equation:
(x - a) squared + y squared = 25
Since circle passes through origin:
a squared = 25
So a = 5 or a = -5
Hence equations:
(x - 5) squared + y squared = 25
or
(x + 5) squared + y squared = 25
Question 10
Find equation of circle passing through points (1,0), (0,1), and (0,-1).
Solution:
General circle equation:
x squared + y squared + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0
Substitute points one by one.
For (1,0):
1 + 0 + 2g + c = 0
For (0,1):
1 + 2f + c = 0
For (0,-1):
1 - 2f + c = 0
Subtract last two equations:
4f = 0
So f = 0
Then c = -1
Then 2g = 0
So g = 0
Final equation:
x squared + y squared - 1 = 0
Visit this link for further practice!!
https://besidedegree.com/exam/s/academic