Chapter 4
Heredity
1. What is Heredity?
Offspring resemble their parents because genes in chromosomes carry hereditary traits.
Study of genes = Genetics.
Chromosomes → DNA → Genes → Traits
Sex chromosomes determine sex (XY = male, XX = female).
2. DNA & RNA
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
Double-stranded, found in nucleus (eukaryotes), cytoplasm (prokaryotes).
Made of nucleotides = sugar + phosphate + nitrogen base (A, T, G, C)
Function: Store and transmit hereditary information
RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
Single-stranded, mainly in cytoplasm
Sugar = ribose; Bases = A, U, G, C
Types: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
Function: Helps synthesize proteins
3. Chromosomes
Chromatin fibers in the nucleus → condense into chromosomes during cell division
Made of DNA + protein
Structure: 2 sister chromatids joined at centromere
Gene = small DNA segment coding a trait
Types:
Autosomes (22 pairs) → Body traits
Sex chromosomes (1 pair) → Male XY, Female XX
Humans:
Somatic cell = 46 chromosomes (2n)
Gamete = 23 chromosomes (n)
4. Cell Division
A. Mitosis (Somatic cells)
1 diploid cell → 2 identical diploid daughter cells
Phases: Karyokinesis (nucleus divides) + Cytokinesis (cytoplasm divides)
Function: Growth, repair, asexual reproduction, maintaining genetic stability
B. Meiosis (Gametes)
1 diploid cell → 4 haploid daughter cells (gametes)
Chromosome number halved (2n → n)
Crossing over creates variation
Function: Sexual reproduction, genetic variation, evolution
5. Fertilization & Sex Determination
Male gamete (sperm: 22+X or 22+Y) + Female gamete (ovum: 22+X) → Zygote (44)
Zygote undergoes mitosis → develops into full organism
Sex determination in humans:
SpermOvumChild22+X22+XFemale (44+XX)22+Y22+YMale (44+XY)Chance of having son or daughter = 50%
Gallery
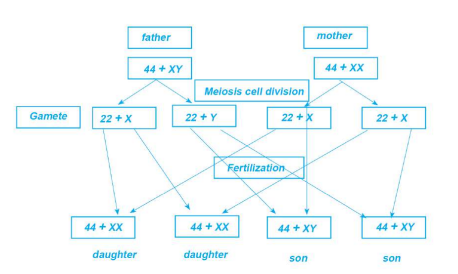
Sex Determination Chart

Structure of RNA
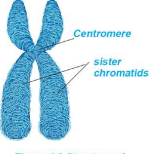
Structure of Chromosome

Structure of DNA
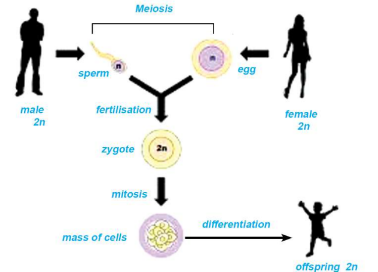
Cell division for the growth and development of living beings
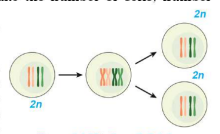
Mitotic cell devision
