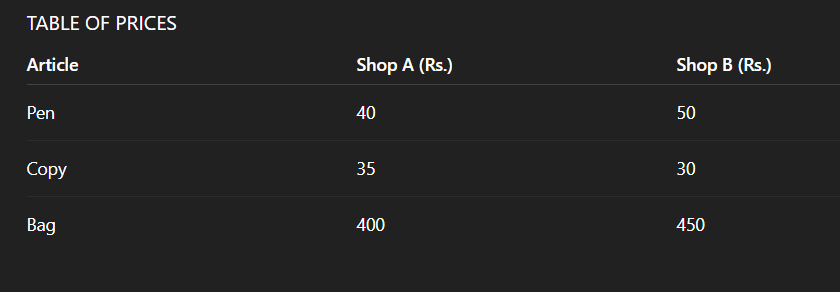
- Table of Prices:
Take the reference of table from image attached below.(Table 1.1)
INTERCHANGING ROWS AND COLUMNS (TRANSPOSE)
Original matrix:
Rows represent articles (Pen, Copy, Bag)
Columns represent shops (A, B)
After interchanging:
Rows represent shops (A, B)
Columns represent articles (Pen, Copy, Bag)
Meaning:
Prices are now compared shop-wise instead of article-wise.
PROFIT PER UNIT
Pen = Rs. 4
Copy = Rs. 6
Bag = Rs. 50
PRICE MATRIX A (3 x 2)
Rows: Pen, Copy, Bag
Columns: Shop A, Shop B
A =
40 50
35 30
400 450
PROFIT ROW MATRIX B (1 x 3)
B =
4 6 50
PRODUCT BA
Multiply profit row with price matrix:
For Shop A:
4×40 + 6×35 + 50×400
= 160 + 210 + 20000
= 20370
For Shop B:
4×50 + 6×30 + 50×450
= 200 + 180 + 22500
= 22880
BA =
20370 22880
INTERPRETATION OF BA
First value represents total profit from Shop A = Rs. 20370
Second value represents total profit from Shop B = Rs. 22880
7.1 DETERMINANT OF A MATRIX
Definition
Determinant is a number associated with a square matrix.
It is denoted by |A|.
DETERMINANT OF 1 x 1 MATRIX
For [a], determinant = a
DETERMINANT OF 2 x 2 MATRIX
For matrix:
a b
c d
Determinant:
|A| = ad − bc
SINGULAR MATRIX
If |A| = 0
Matrix is singular and has no inverse.
NON-SINGULAR MATRIX
If |A| ≠ 0
Matrix has an inverse.
EXAMPLES OF DETERMINANTS
Example 1:
2 1
0 2
|A| = (2×2 − 1×0) = 4
Example 2:
1 2
2 4
|A| = (1×4 − 2×2) = 0 (singular)
Example 3:
5 3
-1 -4
|A| = 5×(-4) − 3×(-1)
= -20 + 3
= -17
3.2 INVERSE OF A MATRIX
Definition
Inverse of matrix A is A inverse such that:
A × A inverse = Identity matrix
CONDITION FOR INVERSE
Inverse exists only if determinant is not zero.
INVERSE OF 2 x 2 MATRIX
For matrix:
a b
c d
Inverse =
1 / (ad − bc) ×
d -b
-c a
EXAMPLE OF INVERSE
Matrix:
4 -7
-3 2
Determinant:
4×2 − (-7×-3) = 8 − 21 = -13
Inverse =
1 / -13 ×
2 7
3 4
3.3 SOLUTION OF LINEAR EQUATIONS (MATRIX METHOD)
General form:
AX = B
Solution:
X = A inverse × B
EXAMPLE 1
3x + y = 8
x + 2y = 7
Solution:
x = 9/5
y = 13/5
3.4 CRAMER’S RULE
For equations:
a1x + b1y = c1
a2x + b2y = c2
D = a1b2 − a2b1
Dx = c1b2 − c2b1
Dy = a1c2 − a2c1
x = Dx / D
y = Dy / D
CRAMER’S RULE EXAMPLE
2x + 3y = 7
4x − y = 5
D = (2×-1 − 4×3) = -2 − 12 = -14
Dx = (7×-1 − 5×3) = -7 − 15 = -22
Dy = (2×5 − 4×7) = 10 − 28 = -18
x = 11/7
y = 9/7
DETERMINANT PROPERTY VERIFICATION
|AB| = |A||B|
Matrix A:
1 2
3 4
Matrix B:
0 1
1 0
|A| = -2
|B| = -1
|A||B| = 2
AB =
2 1
4 3
|AB| = 2
Property verified.
Visit this link for further practice!!
https://besidedegree.com/exam/s/academic
Gallery