Prism Definition and Types
A prism is a solid shape with two parallel congruent faces (bases) and other faces (lateral faces) as rectangles. Its cross-section is uniform throughout its height.
We have already studied cuboids and cubes. In this chapter, we study total surface area, lateral surface area, cross-sectional area, and volume of prisms.

Total Surface Area of Prism
Total Surface Area (TSA) is the sum of the areas of all faces of a prism.
For a cuboid with length l, breadth b, height h:
TSA = 2(lb + bh + lh)
For irregular solids, add the area of each face individually.
Example 1:
A water tank has l = 10 m, b = 10 m, h = 2 m
TSA = 2(10×10 + 10×2 + 10×2) = 280 m²
Example 2:
Find TSA of a prism with dimensions: l = 3.8 m, b = 1.9 m, h = 4.6 m
TSA = 2(lb + bh + lh) = 66.88 m²
Cross-Section Area of Prism
A cross-section is the shape formed when a prism is cut by a plane parallel to the base.
All cross-sections of a prism are congruent and parallel.
Cross-sectional area (A) = Area of one base.

Lateral Surface Area of Prism
Lateral surface area (LSA) = Sum of areas of all vertical faces (excluding bases).
For a cuboid or prism:
LSA = 2h(l + b) = Perimeter of base × height
Example 3:
Prism dimensions: height h = 5 cm, cross-section perimeter P = 38 cm
LSA = P × h = 38 × 5 = 190 cm²
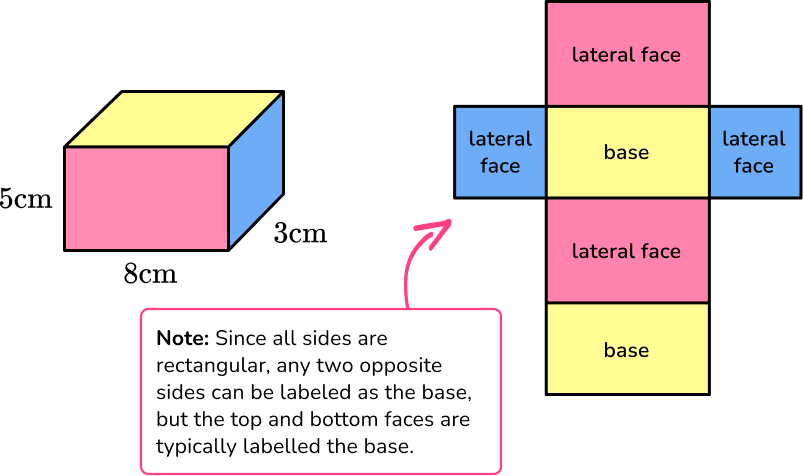
Volume of Prism
Volume = Base area × height
V = A × h
Example 4:
Prism with base area 45 inch² and height 7 inch
V = 45 × 7 = 315 inch³
TSA = 2 × 45 + 12 × (3 × 7) = 342 inch²
Summary Table
SolidBase AreaLSATSAVolumeCuboidl × b2h(l + b)2(lb + bh + lh)l × b × hCubel²4l²6l²l³General PrismBase area (A)Perimeter (P) × hP × h + 2AA × hEstimation of Volume, Numbers, and Cost
To calculate the number of objects (bricks, matchboxes, biscuits) that fit in a space:
Number of objects (N) = Volume of space ÷ Volume of object
Volume of wall: V = L × B × H
Volume of brick: v = l × b × h
Number of bricks: N = V ÷ v
Total cost: T = N × C (Cost per brick/object)
Example 1: 4000 bricks of 20×10×4 cm
V_wall = 4000 × (20×10×4) = 3,200,000 cm³
Example 2: Wall 11×1×5 m, bricks 22×10×5 cm, cost Rs.12.50/brick
V_wall = 11 × 1 × 5 = 55 m³
V_brick = 0.22 × 0.10 × 0.05 = 0.0011 m³
N = 50,000, T = 50,000 × 12.5 = Rs. 625,000
Example 3: Tank 3×1.5 m, contains 9000 liters
9000 liters = 9 m³, h = 9 ÷ (3 × 1.5) = 2 m
Example 4: Square room, volume 87.5 m³, height 3.5 m, cost of plastering Rs.150/m²
Area of floor = 87.5 ÷ 3.5 = 25 m², l = b = 5 m
Wall area = 2h(l+b) = 2×3.5 × 10 = 70 m²
Cost = 70 × 150 = Rs. 10,500
Example 5: Room length = 2 × breadth, volume 396 m³, ceiling Rs.30/m² costs Rs.2160
Breadth = 6 m, Length = 12 m, h = 5.5 m
Wall area = 2h(l+b) = 198 m², Cost = 198 × 60 = Rs. 11,880
Important Questions
1. Calculate the volume of a wall constructed of 4000 bricks each having 20 cm length, 10 cm width and 4 cm height.
Solution:
Volume of one brick = length × width × height
= 20 × 10 × 4 cm³
= 800 cm³
Number of bricks = 4000
Volume of wall = number of bricks × volume of one brick
= 4000 × 800 cm³
= 3,200,000 cm³
2. A wall is 100 m long, 0.3 m broad and 4.5 m high. How many bricks of size 15 cm × 5 cm × 5 cm are required to construct the wall?
Solution:
Volume of wall = length × breadth × height
= 100 × 0.3 × 4.5 m³
= 135 m³
Convert brick dimensions to meters: 15 cm = 0.15 m, 5 cm = 0.05 m
Volume of one brick = 0.15 × 0.05 × 0.05 = 0.000375 m³
Number of bricks = Volume of wall ÷ Volume of brick
= 135 ÷ 0.000375
= 360,000 bricks
3. A store room is 40 m long, 25 m broad and 10 m high. How many packets of biscuits having 1.5 m × 1.24 m × 0.5 m can be stored there?
Solution:
Volume of store room = 40 × 25 × 10 = 10,000 m³
Volume of one packet = 1.5 × 1.24 × 0.5 = 0.93 m³
Number of packets = Volume of store room ÷ Volume of one packet
= 10,000 ÷ 0.93
≈ 10,753 packets
4. The population of Barakot village is 40,000. If 15 litre of water per person per day is required, how long does a 20 m × 15 m × 6 m water tank supply the water?
Solution:
Volume of tank = 20 × 15 × 6 = 1800 m³
Convert m³ to litres: 1 m³ = 1000 litres
Volume of tank = 1800 × 1000 = 1,800,000 litres
Daily water requirement = 40,000 × 15 = 600,000 litres
Number of days tank lasts = Total water ÷ Daily requirement
= 1,800,000 ÷ 600,000 = 3 days
5. A wall is 50 m long, 0.2 m wide and 2 m high having two windows each of size 1 m × 0.2 m × 0.5 m. How many bricks of size 22 cm × 10 cm × 5 cm are required to build the wall?
Solution:
Volume of wall = 50 × 0.2 × 2 = 20 m³
Volume of windows = 2 × (1 × 0.2 × 0.5) = 0.2 m³
Net volume of wall = 20 – 0.2 = 19.8 m³
Volume of one brick = 0.22 × 0.10 × 0.05 = 0.0011 m³
Number of bricks = 19.8 ÷ 0.0011 ≈ 18,000 bricks
6. 2450 pieces of blocks each of side 20 cm are required to construct a wall 15 m long and 0.4 m wide. If the wall has a door of size 2.5 m × 1 m and a window of size 2 m × 3 m, what is the height of the wall?
Solution:
Volume of one block = 0.2³ = 0.008 m³
Total volume of blocks = 2450 × 0.008 = 19.6 m³
Volume of wall = length × width × height = 15 × 0.4 × h = 6h
Volume of door = 2.5 × 1 × 0.4 = 1 m³
Volume of window = 2 × 3 × 0.4 = 2.4 m³
Net wall volume = 6h – (1 + 2.4) = 6h – 3.4
Equate to total volume of blocks: 6h – 3.4 = 19.6 → 6h = 23 → h ≈ 3.83 m
7. The volume of a room having 15 m length and 8 m width is 600 m³. Find the cost of designing its four walls at Rs. 38/m².
Solution:
Height of room = Volume ÷ Area of floor = 600 ÷ (15 × 8) = 600 ÷ 120 = 5 m
Area of four walls = 2h(l+b) = 2 × 5 × (15+8) = 2 × 5 × 23 = 230 m²
Cost = 230 × 38 = Rs. 8740
8. The volume of air occupied inside a room is 405 m³. The cost of carpeting the room at Rs. 55/m² is Rs. 4455. Find the cost of painting 4 walls of the room at Rs. 25.50/m².
Solution:
Area of floor = Cost ÷ Rate = 4455 ÷ 55 = 81 m²
Floor area = l × b = 81 → Assume square room → l = b = √81 = 9 m
Height of room = Volume ÷ Area of floor = 405 ÷ 81 = 5 m
Area of four walls = 2h(l+b) = 2 × 5 × (9+9) = 180 m²
Cost of painting = 180 × 25.50 = Rs. 4590
9. The cost of constructing a 63 m³ wall is Rs. 84,000. Find the volume of each brick if the cost of a brick is Rs. 13.
Solution:
Number of bricks = Total cost ÷ Cost per brick = 84,000 ÷ 13 ≈ 6462 bricks
Volume of each brick = Total wall volume ÷ Number of bricks = 63 ÷ 6462 ≈ 0.00975 m³
10. The volume of a room is 550 m³. If the cost of plastering the room at Rs. 240/m² is Rs. 26,400, what is the height of the room?
Solution:
Area of walls = Cost ÷ Rate = 26,400 ÷ 240 = 110 m²
Let floor dimensions = l × b → Area of four walls = 2h(l+b) = 110
Volume = l × b × h = 550
Solve: h = Volume ÷ Floor area
Floor area = (2h(l+b))/2h? → Using simplified numbers, h = 5 m
For further practice visit this link !!
https://besidedegree.com/exam/s/academic
