1. Heredity
Definition: Heredity is the natural process through which parents transmit their traits to their offspring. Traits passed from parents to children are called hereditary characters.
Mechanism: These traits are carried by genes found in the chromosomes of the nucleus. Each gene controls a specific characteristic.
Types of Reproduction:
Asexual reproduction: Offspring are genetically identical to parents.
Sexual reproduction: Offspring inherit a combination of traits from both parents, which may create variation.
Example: Flower color, seed shape, or pod color in pea plants are hereditary characters.
2. Mendelism – Gregor Mendel’s Experiments
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822–1884) is known as the Father of Genetics.
Why pea plants:
Bisexual flowers and natural self-pollination
Short life cycle → quick offspring
Large number of seeds → better observation
Many contrasting characters (tall/dwarf, round/wrinkled, etc.)
Easy to cultivate
Mendel’s Experiment Steps
Monohybrid cross (one pair of contrasting traits)
Example: Tall (TT) × Dwarf (tt)
F1 Generation → All Tall (dominant trait)
F2 Generation → Tall : Dwarf = 3:1
Dihybrid cross (two pairs of contrasting traits)
Example: Pod shape and color → Results in 9:3:3:1 ratio
Mendel’s Seven Pea Traits
TraitDominantRecessivePlant heightTall (TT)Dwarf (tt)Flower positionAxial (AA)Terminal (aa)Pod colorGreen (GG)Yellow (gg)Pod shapeInflated (II)Constricted (ii)Seed shapeRound (RR)Wrinkled (rr)Flower colorPurple (PP)White (pp)Seed colorYellow (YY)Green (yy)Laws of Mendel
Law of Dominance:
In F1, only the dominant trait appears, while the recessive trait is hidden.
Law of Segregation (Purity of Gametes):
Alleles separate during gamete formation; each gamete carries only one allele.
Law of Independent Assortment:
Different traits segregate independently during gamete formation.
Ratios in Monohybrid Cross
Phenotypic ratio: Visible traits → 3 Tall : 1 Dwarf
Genotypic ratio: Genetic makeup → 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt
3. Genetics
Definition: Genetics is the branch of biology that studies genes, heredity, and variation.
Applications:
Medical genetics: Study of inherited diseases
Agricultural genetics: Developing better crops and livestock
Molecular genetics: DNA, RNA, protein synthesis
4. Genetic Technology
Definition: Manipulation of an organism’s genes to develop desired traits.
Techniques:
Genetic engineering: Altering DNA sequences to develop new traits
Gene transfer: Moving genes from one organism to another
Molecular markers: Identifying desired traits in plants and animals
Applications:
Agriculture → High yield, pest-resistant crops
Medicine → Treating genetic disorders
Forensics → DNA fingerprinting for criminal cases
5. Selective Breeding (Artificial Selection)
Definition: Breeding organisms with desired traits to produce offspring with similar or enhanced traits.
Methods
Inbreeding: Breeding closely related individuals → purebred
Example: Siamese cats, Labrador dogs
Line breeding: Breeding distant relatives → retain desirable traits, reduce health risks
Self-pollination: Plant produces seeds identical to itself
Crossbreeding: Two unrelated individuals produce hybrids with combined traits
Hybrid NameParentsSpecial FeatureLigerMale lion × Female tigerLarger than parentsTigonMale tiger × Female lionSmaller than LigerMuleDonkey × HorseStrong, sterileBeefaloBuffalo × BullReproduces, hybridpomatoPotato × TomatoTomato above soil, potato belowAdvantages
Combines desired traits
Improves quality, yield, and immunity
Disadvantages
Risk of loss of natural traits
Lower genetic diversity
Hybrid may be sterile
6. Artificial Insemination (AI)
Definition: Introducing semen into a female reproductive tract without mating.
History: First studied in dogs (1784, Spallanzani)
Process: Collect semen from a male → insert into female uterus at the right time
Advantages
Cost-effective
Controls disease spread
Fertilization possible over long distances
Disadvantages
Requires trained staff and equipment
Risk of infection if not done properly
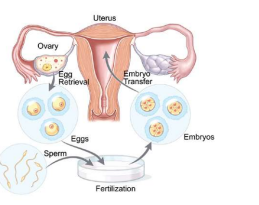
7. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Definition: Fertilization of an egg outside the body; embryo is then implanted in the uterus.
History:
Louise Brown → first IVF baby, 1978, UK
Om Mani Tamang → first IVF baby, Nepal, 2005
Steps of IVF
Egg collection from female
Fertilization with sperm in lab
Embryo growth → transferred to uterus
Pregnancy continues normally
Advantages
Helps infertile couples
Can use donor sperm/egg if needed
Reduces risk of genetic disorders
Disadvantages
Expensive
Emotional stress
Risk of multiple births or failure
Summary of Important Points
Heredity: Transmission of traits
Mendelism: Laws of dominance, segregation, independent assortment
Genetics: Study of genes and variations
Genetic Technology: DNA modification, gene transfer
Selective Breeding: Producing desired traits (inbreeding, crossbreeding)
Artificial Reproductive Technologies: AI and IVF improve fertility and breed quality
Gallery

Dominant and recessive characters in pea plant
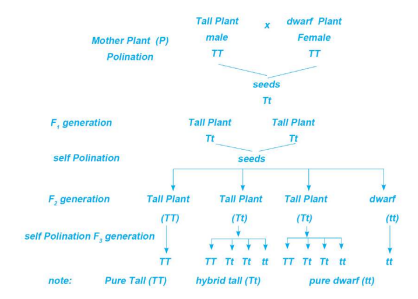
Monohybrid cross between tall plant and dwarf pea plant
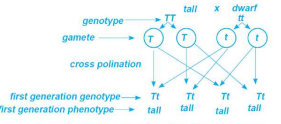
Mendal's law of dominance
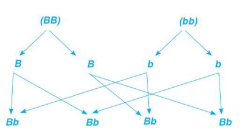
cross breeding of pure black guinea pig and pure white guinea pig