Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Introduction to Television Technology Evolution
Three Types of Television Systems
1. Antenna TV (Traditional)
- Oldest technology
- Signal Type: Analog signals received through antenna
- Audio-Visual Quality: Poorest among all three types
- How it works:
- Waves emitted from transmitter travel through air
- Energy is lost to surroundings during transmission
- Less potential difference (p.d.) generated on antenna
- Weakened electrical current in antenna wire
- Current acts as modulated signal for TV broadcasting
2. Cable TV
- Technology: Cable-based transmission
- Signal Type: Modulated analog signals through wires
- Components:
- Cable splitter
- Cable modem (needed to use computer as TV)
- Quality: Better than antenna TV
- Popularity: Very popular before Dish TV
3. Dish TV (Satellite TV)
- Modern technology
- Signal Type: Digital signals received from satellite
- Quality: Best audio-visual quality
- Current Status: Has replaced traditional TV systems
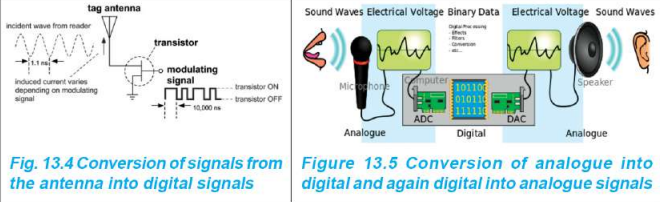
Signal Conversion Process
In All TV Systems:
- Signals must be converted to digital signals by internal TV circuits
- Digital signals transmit audio-visual content
- For viewing: Digital signals → Analog signals (visible and audible)
Necessity: Device needed that can:
- Convert analog signals to digital signals (ADC)
- Convert digital signals back to analog signals (DAC)
Digital Signals
Activity 13.1: Understanding Digital Signals
Setup:
- 5V AC source + bulb + switch + conducting wire
- Switch ON → 5V potential difference → High signal (1)
- Switch OFF → 0V potential difference → Low signal (0)
Observation:
- Switching creates on-off signals
- Graph shows discrete voltage levels (0V or 5V)
- This is a digital signal
Definition of Signal
Signal: A physical quantity that changes with time
Digital Signal Characteristics
Representation:
- Only two digits: 0 and 1
- Uses binary system
- Combination of binary digits represents digital signals
Examples:
- 1 binary digit: 0 or 1 (2 combinations)
- 2 binary digits: 00, 01, 10, 11 (4 combinations)
- 3 binary digits: 000, 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, 110, 111 (8 combinations)
Visual Representation:
- Square wave pattern
- Discrete levels (0V or 5V)
- Sudden transitions between levels
- No intermediate values
Analog Signals
Definition
Analog Signal: A signal that indicates constantly changing physical quantity
Characteristics
- Continuously changes with time
- Sine wave pattern
- Smooth transitions
- Range: Example: -5V to +5V
- Has peaks (maximum positive) and valleys (maximum negative)
Example
If switch in Activity 13.1 was never turned off:
- Voltage increases and decreases continuously
- Creates smooth sine wave
- This is an analog signal
Computer Memory and Storage
Data Storage in Computers
- Digital signals indicate different data
- Data stored in computer memory
- Can store permanently in large amounts
- Formats: Text, graphics, audio, video
Important Terms
Bit (Binary Digit):
- Smallest form of data on computer
- Can be either 0 or 1
Byte:
- Group of eight bits
- Works as single unit of data in computer
Comparison: Digital vs Analog Signals
FeatureAnalog SignalDigital SignalDefinitionConstantly changing physical quantityPhysical quantity changing in segmentsTime VariationChanges continuouslyChanges by two fixed valuesWave FormSine waveSquare waveVoltage RangeExample: -5V to +5VExample: 0V or 5VConverterADC (Analog to Digital Converter)DAC (Digital to Analog Converter)Example DeviceTemperature sensor (analog input)Playing music on computer (digital to analog)Signal Transmission
Definition
Signal Transmission: The process of signal transformation through a medium or channel
Types of Signals Used
Analog Transmission (Traditional):
- Sound waves used in communication
- Landline phones use analog signals through wires
- Radio broadcasts (medium wave, short wave)
Problems with Analog Transmission:
- External effects (mixing of other waves)
- Atmospheric interference
- Signal becomes unclear
- Security issues (illegal recording possible)
- Signal distortion
Digital Transmission (Modern):
- Analog signals digitalized using various technologies
- Makes signals more clear and distinct
- Data doesn't change
- Better protection and security
Advantages of Digitalization
- Signals remain clear
- Data can be stored, transmitted, and recreated using 0s and 1s
- Data processing is easier
- Very low possibility of error
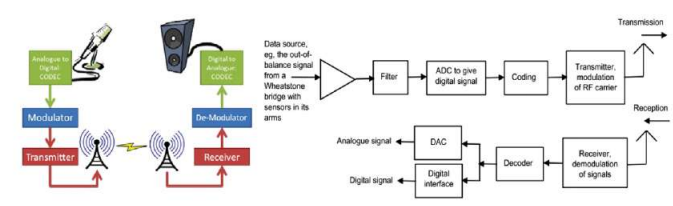
Components of Digital Communication System
Complete Process Flow
Transmission Side:
- Source → 2. Input Transducer → 3. Encoder → 4. Modulator → 5. Channel
Reception Side: 6. Channel → 7. Demodulator → 8. Decoder → 9. Output Transducer → 10. Output Signal
Detailed Explanation of Each Component
(a) Source
- Origin of signal
- Example: Sound waves, analog signals
(b) Input Transducer
- Function: Converts received signals into electrical signals
- Example: Microphone converts sound into electricity
(c) Encoder
- Function: Compresses data to minimum number of bits
- Purpose: Effective utilization of available frequency range (Bandwidth)
(d) Modulator
- Function: Modulates data to be transmitted by carrier
- Process: Converts digital signals to analog signals for transmission
- Directs signals to channel/medium
(e) Channel (Medium)
- Function: Provides pathway for analog signals
- Connects transmitter to receiver
(f) Demodulator
- Location: First step at receiver side
- Function: Demodulates received signal
(g) Decoder
- Function: Re-digitizes demodulated signals
- Purpose: Removes possible errors in final output
(h) Output Transducer
- Function: Converts decoded signals to original physical signal
- Changes electrical signals to physical output
- Example: Loudspeaker converts current to sound
(i) Output Signal
- Final result of overall transmission process
- Example: If input was sound waves, output is sound waves
Types of Transmission
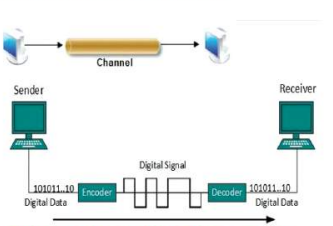
Baseband Transmission
Definition: Transmission of digital signals through channels WITHOUT conversion to analog signals
Characteristics:
- Sending and receiving done simultaneously in same channel
- Used for short-distance transmission
- Direct digital signal transmission
- Example: Connecting two computers with cables
Process Flow:
Digital Data → Encoder → Channel → Decoder → Digital Data (101011...) (101011...)
Broadband Transmission
Definition: Transmission of digital signals AFTER converting to analog signals
Common Usage: "Broadband internet" = High-speed internet
Characteristics:
- Requires modulation
- Used for long-distance transmission
- Analog signals transmitted as optical or electromagnetic waves
- Various transmission frequencies available
Channel Configuration:
- Two separate channels for sending and receiving, OR
- Two separate cables
Modulation Types (for digital signals):
- ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying): Changes amplitude
- FSK (Frequency Shift Keying): Changes frequency
- PSK (Phase Shift Keying): Changes phase
Activity 13.2: Test internet speed at www.speedtest.net
Advantages of Digital Transmission
- Low Deterioration: Noise effects very less in digital signals
- Reliability: Circuits much more reliable
- Cost-Effective: Cheap and easy to design digital circuits vs analog
- Less Interference: Less signal overlap and cross-talk
- Stable Properties: Signal properties don't change in normal conditions
- Security: Information secured through encoding and compression
- Error Correction: Codes for finding and correcting errors reduce transmission errors
Influence of Digital Technology on ICT Development
Overall Impact
Digital technology has:
- Increased quality of information and technology
- Increased prevalence of use
- Enabled modernization of various systems
(a) Digital Telecommunication
Benefits:
- Fast communication possible
- Multiple telephone calls through single channel/bandwidth
- Efficient use of resources
Process:
Information Source → Analog-to-Digital Conversion → Encoding → Modulation → Multiplexing → Channel → Demultiplexing → Demodulation → Decoding → Digital-to-Analog Conversion → Information
(b) Digital Media
Definition: Electronic devices used for communication
Capabilities:
- Creating new digital media
- Watching news online
- Online information transmission
- Content creation and sharing
Examples:
- Smartphones
- Tablets
- Computers
- Smart TVs
(c) Digital TV
Types of Digital TV:
- Terrestrial TV: Transmitted by terrestrial broadcasters
- Satellite TV: Via satellite (MSO - Multiple System Operators)
- Cable TV: Through cable headend
- Mobile/Portable TV: Car audio, PDA devices
Features:
- Different shapes and sizes
- Unique characteristics
- High-Definition (HD) quality
- Latest digital technology
- Dish TV: Expanded service throughout country
Digital Technologies in Daily Life
Common Applications
- Infrared and Digital Thermometer: Health monitoring
- Calculator: Mathematical calculations
- Online Newspaper: Digital news access (e.g., www.gorkhapatraonline.com)
- Digital Wallet: Cashless payments
- Online Library: Digital textbooks and materials (e.g., CDC library)
- Speedometer: Vehicle speed measurement
- Digital Camera: Photography and videography
- Smartwatch: Time, fitness tracking, notifications
- Calendar: Digital scheduling
Fields of Application
- Education: E-learning, digital libraries
- Health: Digital thermometers, health apps
- Entertainment: Games, music, videos
- Finance: Digital payments, online banking
Positive Effects of Digital Technology
1. Digital Library
- Digital versions of textbooks available
- Develops book-reading habits
- Example: CDC library with textbooks and reference materials
2. Online Newspapers
- Accessible with internet and smartphone
- Example: www.gorkhapatraonline.com
- Up-to-date news anytime, anywhere
3. Digital Payment
- Benefit: No need to carry physical money
- Methods:
- QR code scanning
- Bank account transfers
- Uses:
- Shopping payments
- Tax payments
- Bus and plane ticket booking
- Bill payments
4. Online Business
- Promote business materials through internet
- Sell products online
- Wider market reach
- E-commerce platforms
5. Social Networks
- Express opinions publicly
- Connect people digitally across distances
- Community building
- Information sharing
6. Entertainment
- Various games available
- Music applications
- Video streaming
- Content consumption
Negative Effects of Digital Technology
1. Social Behavior Changes
- Excessive online time affects social interaction
- Changes in communication patterns
- Reduced face-to-face interaction
2. Cybercrime and Privacy Issues
- Crimes committed through social media
- Affects personal, family, and social life
- Reputation damage → Mental stress
- Privacy violations
3. Economic Impact
- Reduced consumption of physical materials
- Loss of business opportunities for traditional businesses
- Job displacement
4. Physical Health Problems
- Lack of physical exercise
- Obesity in children and adults
- Weakness and poor fitness
- Vision problems from screen time
- Insomnia (sleep disorders)
5. Mental Health Issues
- Violence and murder in digital games
- Adverse effects on mental health
- Social well-being affected
- Spread of antisocial activities
- Depression and anxiety
- Low self-esteem
- Social isolation and loneliness
- Aggressiveness
6. Cybercrime
- Misuse of digital technology
- Harm to others
- Identity theft
- Online fraud
- Hacking
Digital Citizenship
Netizen (Digital Citizen)
Definition: A person who actively uses and engages on the internet
Etymology: "Netizen" = "Net" (Internet) + "Citizen"
Concept:
- All people have same rights to use internet
- Active participation in online world
- Citizen of globally connected internet
Digital Citizenship
Definition: The citizenship of netizens in the virtual world of the internet
Impact:
- Helps improve overall internet world
- Creates concept of "Global Village"
- Connects citizens worldwide through:
- Telephone
- Internet phone calls
- Social network communication
- Various communication channels
Characteristics of a Good Netizen
Internet Etiquette
Online Behavior Standards:
- Socially acceptable behavior online
- Polite and civilized language in:
- Online dialogues
- Email communication
- Public comments on social networks
- Personal respect and respect for others
- Treat everyone with respect even without face-to-face meeting
Content Responsibility
Important Principles:
- Permanence: Anything posted online is permanent
- Intellectual Property:
- Internet content is someone else's product
- Unauthorized use not permitted
- Must cite source if using material
- Authenticity: Use real information in profiles
Digital Duties
- Follow internet etiquette
- Respect intellectual property
- Maintain appropriate online behavior
- Contribute positively to online community
Online Reputation
Personal Online Reputation
Definition: How a person is perceived in the digital/online world
Managing Personal Reputation
Profile Authenticity:
- Use real name
- Use real photo
- Provide accurate public details
- Shows authenticity and reliability
Consistency:
- Same username across all social media profiles
- Consistent identity
Content Quality:
- Posts, comments, and shares reflect:
- Person's knowledge
- Expertise
- Character
- Values
Security Measures:
- Careful about internet security
- Strong privacy settings on social networks
- Poor settings lead to:
- Password theft
- Harmful content posting
- Reputation damage
Organizational Online Reputation
Company/Institution Presence:
- Official website with published information
- Social media pages with regular updates
- Follower count indicates credibility
- Presence on major sites and networks required
Reputation Management:
- Timely resolution of comments
- Addressing complaints promptly
- Professional communication
- Consistent branding
Digital Wellbeing
Definition
Digital Wellbeing: The state of being healthy mentally, physically, socially, and emotionally by balancing time spent on online and offline activities
Why Digital Wellbeing Matters
Health Problems from Excessive Screen Time:
Physical Issues:
- Obesity (lack of physical activity)
- Insomnia (sleep problems)
- Vision problems (eye strain)
- Poor posture
- Lack of exercise
Mental Issues:
- Mental stress
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Dishonesty
- Low self-esteem
Social/Emotional Issues:
- Social isolation
- Loneliness
- Aggressiveness
- Reduced face-to-face interaction
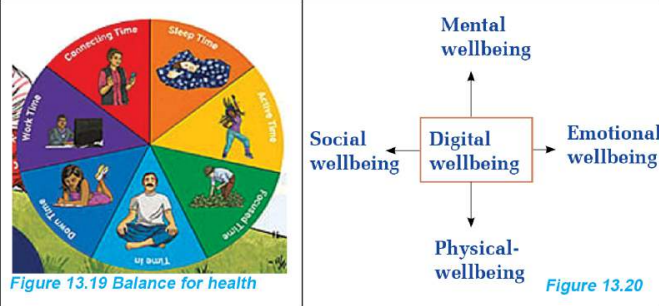
Four Dimensions of Digital Wellbeing
- Physical Wellbeing: Body health, exercise, sleep
- Mental Wellbeing: Psychological health, stress management
- Social Wellbeing: Relationships, interactions
- Emotional Wellbeing: Feelings, emotional balance
Time Balance Components
Daily Time Management:
- Sleep Time: Adequate rest
- Work Time: Productive activities
- Active Time: Physical exercise
- Focused Time: Concentrated work/study
- Down Time: Relaxation
- Connecting Time: Social interaction (online/offline)
Cautions for Digital Wellbeing
Activity 13.3: Self-Assessment
- Track household digital device usage
- Discuss long-term effects
- Note possible consequences
Problems from Digital Addiction
- Chaotic lifestyle
- Poor time management
- Health deterioration
- Relationship problems
Digital Wellbeing Skills Required
- Awareness of effects
- Understanding of unnecessary use consequences
- Self-regulation abilities
Healthy Habits to Develop
- Separate screen time
- Designated times for device use
- Screen-free periods
- Set time limits
- Specific duration for social media
- App timers
- Turn off notifications
- During work
- During study
- During sleep
- Regular breaks
- Eye rest
- Physical movement
- Stretching
Digital Wellbeing Applications
Purpose: Help reduce screen time and manage digital usage
Available Apps:
- Beta
- Action Dash
- Digital Detox
- Microsoft Launcher
- Digital Wellbeing (Android)
Features:
- Track daily usage time
- Show app-wise usage
- Set time limits
- Turn off notifications
- Schedule app usage
- Bedtime mode
Activity 13.4: Using Digital Wellbeing App
- Download from Play Store
- Install and open
- Observe daily usage statistics
- Set time limits
- Configure notifications
- Explore features
Educational Use of Digital Technology
Safe Internet Use for Learning
Resources:
- Educational websites
- Online courses
- Video tutorials
- Example: https://www.youtube.com/c/NCEDVirtual (audio-visual content for different subjects)
Caution: Maintain digital wellbeing while learning online
Creating Audio and Audio-Visual Materials
Audio Content Creation
Recording Method:
- Use computer microphone
- Use smartphone microphone
- Record sound directly
File Formats: MP3, WAV, WMA
Audio-Visual (Video) Content Creation
Recording Devices:
- Smartphone camera
- Digital camera
- Computer webcam
Activity 13.5: Video Recording Example
- Record spring balance with 500g mass
- Drop from height
- Record in slow motion
- Observe needle position
- Demonstrates scientific principle
Video File Formats:
- MP4: Most common
- 3GP: Mobile format
- SVI: Samsung video
- MOV: QuickTime format
Video Editing
Purpose of Video Editing
- Cut unnecessary segments
- Combine multiple clips
- Create complete video file
- Enhance quality
- Add effects
Software Options
Computer Software:
- Adobe Premiere Pro (Professional)
- Filmora (User-friendly)
- Windows Video Editor (Built-in)
Mobile Applications:
- Various apps available in Play Store
- Can be downloaded and installed
Video Editing Process (Activity 13.6)
Part (a): Video Cutting
Step-by-Step Process:
- Launch Video Editor
- Click search bar
- Type "Video Editor"
- Open application
- Create New Project
- Click "New video project"
- Type project name (e.g., "Class 10 ICT")
- Click OK
- Add Video
- Select video from computer memory
- Drag to project library
- Drag to editing panel
- Trim Video
- Select video in editing panel
- Click "Trim" button
- Play video to find cut points
- Set Cut Points
- Use two blue drag bars
- Set start time
- Set end time
- Check clip length
- Click "Done"
- Export Video
- Select cut clip
- Click "Finish video"
- Click "Export"
- Choose save location (e.g., Desktop)
- Save file
Part (b): Video Joining
Step-by-Step Process:
- Collect Clips
- Copy all clips to single folder
- Organize files
- Open Video Editor
- Launch software
- Create new project
- Add Multiple Files
- Select all videos to join
- Add to project library
- Drag all to editing panel
- Arrange Clips
- Order clips as desired
- Check transitions
- Join Videos
- Select all files in editing panel
- Click "Finish video"
- Export Combined Video
- Choose save location
- Export file
Mobile Video Editing
Process:
- Open video from gallery
- Click "Edit" icon
- Click "Cut" or "Crop" icon
- Make edits
- Save edited video
If No Editing App:
- Download from Play Store
- Install application
- Use for editing
Audio Editing
Similar Process to Video Editing
- Use audio editing software/applications
- Cut, trim, merge audio files
Audio File Formats
- MP3: Most common
- WAV: High quality
- WMA: Windows Media Audio
Software Options
Computer Software:
- Audacity (Free, professional)
- Download from: www.audacityteam.org
- MP3 Cutter
- Download from official sources via Google search
Mobile Applications:
- Available in App Store
- Available in Play Store
- Various options for different platforms
Download and Installation
- Search for software
- Download from official source
- Install on computer/smartphone
- Open and use for editing
Summary of Key Concepts
Signal Types
- Analog: Continuous, sine wave, -5V to +5V
- Digital: Discrete, square wave, 0V or 5V
TV Evolution
- Antenna TV → Cable TV → Dish TV
- Analog → Modulated signals → Digital signals
Digital Communication
- Better quality than analog
- Less affected by interference
- Requires larger bandwidth
- Enables coding and security
Transmission Types
- Baseband: Short distance, no modulation
- Broadband: Long distance, requires modulation
Digital Technology Impact
- Positive: Libraries, payments, business, entertainment
- Negative: Health issues, cybercrime, addiction
Digital Citizenship
- Netizen: Active internet user
- Requires etiquette and responsibility
- Online reputation matters
Digital Wellbeing
- Balance online/offline time
- Use wellbeing applications
- Maintain physical, mental, social, emotional health
Content Creation
- Audio recording and editing
- Video recording and editing
- Various software and apps available
Gallery
Baseband Broadcasting Channel
Digital Signal Transmission Process and Block Picture
Conversion of signals