Physiological Structure and Life Processes: Blood Circulation in Human Body
1. Circulatory System
Definition: The system that transports blood, oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and wastes throughout the body.
Main organ: Heart
Other components: Blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries), blood
Function:
Transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones to all cells
Removes wastes (CO₂, urea) to excretory organs
Connects other organ systems (digestive, respiratory, endocrine)
2. Blood
Definition: Red-colored connective tissue that circulates in the body.
Composition:
Plasma (55%): pale yellow liquid, 80–90% water + dissolved substances (proteins, carbs, salts, hormones, enzymes)
Blood cells (45%): Red blood cells, White blood cells, Platelets
Functions:
Transportation: Oxygen, CO₂, nutrients, hormones, wastes
Regulation: Body temperature, water balance, pH
Protection: WBCs fight infection, platelets clot blood
Blood Corpuscles
a. Red Blood Cells (RBC / Erythrocytes)
Biconcave, nucleus-free, red
Contain hemoglobin (iron + protein globin) → binds O₂ and CO₂
Life span: 90–120 days
Produced in bone marrow, destroyed in liver & spleen
Deficiency → Anemia; Excess → Polycythemia
b. White Blood Cells (WBC / Leucocytes)
Larger, nucleated, no hemoglobin
Types:
Granular: Neutrophil, Eosinophil, Basophil
Non-granular: Lymphocytes, Monocytes
Life span: ~2 weeks
Function: Fight infections → “soldiers of the body”
Deficiency → Leukopenia, Excess → Leukemia
c. Platelets (Thrombocytes)
Smallest, non-nucleated
Function: Blood clotting (with fibrinogen)
Deficiency → Hemophilia, Excess → Thrombocytosis
3. Blood Groups
Determined by antigens on RBC surface: A, B, AB, O
Also contains Rh factor (D antigen) → Positive (+) / Negative (–)
Total blood groups = 8 (A+, A–, B+, B–, AB+, AB–, O+, O–)
Importance: Compatibility in blood transfusions
4. Heart
Definition: Muscular organ that pumps blood to all parts of the body.
Size: About a fist, ~300 g
Location: Thoracic cavity, slightly left
Protected by pericardium (double-layered membrane)
Structure:
Four chambers: Right & Left Auricle (atrium), Right & Left Ventricle
Septum: Prevents mixing of oxygenated & deoxygenated blood
Valves: Tricuspid, Bicuspid/Mitral, Pulmonary, Aortic
Blood vessels:
Veins → bring blood to heart (superior & inferior vena cava, pulmonary veins)
Arteries → carry blood from heart (aorta, pulmonary artery)
Function: Pump blood → supplies oxygen/nutrients and removes wastes
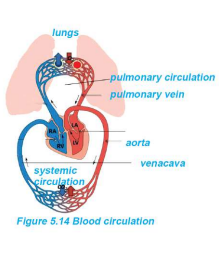
Blood Circulation
1. Systemic Circulation:
Oxygenated blood → Left ventricle → aorta → body → deoxygenated blood → right auricle via veins
2. Pulmonary Circulation:
Deoxygenated blood → Right ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs → oxygenated blood → left auricle via pulmonary veins
5. Heartbeat & Pulse
Heartbeat: Rhythmic contraction & relaxation of heart
Pulse: Expansion of artery walls as blood flows
Normal rate: 60–100/min
Bradycardia: <60/min, Tachycardia: >100/min
6. Blood Vessels
Arteries: Thick, muscular, no valves, carry blood away from heart
Veins: Thin-walled, valves prevent backflow, carry blood to heart
Capillaries: Microscopic, allow exchange of gases, nutrients, and wastes
7. Blood Pressure
Definition: Pressure exerted by blood on artery walls
Systolic: During ventricular contraction
Diastolic: During ventricular relaxation
Normal: 120/80 mmHg
High BP (Hypertension): >140/90 mmHg
Causes: Obesity, stress, salty/fatty food, smoking, lack of exercise
Prevention: Healthy diet, exercise, stress management
8. Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)
Definition: Sudden blockage of blood flow to heart → tissue damage
Causes: Narrowed coronary arteries due to cholesterol/fat deposits (plaque)
Symptoms: Chest pain, shortness of breath, cold sweat, nausea
Treatment:
Medical: Oxygen supply, blood thinners
Surgical: Angioplasty & stenting, Coronary artery bypass
9. Disorders Related to Blood Circulation
Diabetes (Hyperglycemia): High blood sugar due to insufficient insulin
Symptoms: Thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision
Prevention: Balanced diet, exercise, active lifestyle
High Uric Acid (Hyperuricemia): Excess uric acid → joint pain, kidney stones
Causes: Purine-rich diet, low water intake
Prevention: Exercise, water intake, avoid fatty foods
Hypertension: High blood pressure
Prevention: Healthy lifestyle, avoid alcohol & smoking, exercise
Component% in BloodStructureFunctionPlasma55%Pale yellow liquid, 80-90% waterTransport nutrients, hormones, waste; maintain pH & temp; blood clottingRed Blood Cells (RBC)45%Biconcave, no nucleus, redTransport O₂ & CO₂ via hemoglobinWhite Blood Cells (WBC)<1%Nucleated, irregular shapeFight infections (immunity)Platelets<1%Small, non-nucleatedBlood clotting3. Blood Circulation
A. Systemic Circulation
Left Ventricle → Aorta → Arteries → Capillaries (body cells) → Veins → Vena Cava → Right Auricle
Function: Deliver O₂ & nutrients to cells, remove CO₂ & wastes
B. Pulmonary Circulation
Right Ventricle → Pulmonary Artery → Lungs → Pulmonary Vein → Left Auricle
Function: Exchange CO₂ for O₂ in lungs
4. Blood Vessel Types
Heart → Artery → Arteriole → Capillaries → Venule → Vein → Heart
Gallery
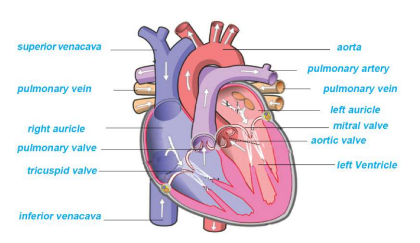
Internal structure of heart