1. Introduction
A file is a collection of related data, information or instructions stored on a secondary storage device (like a hard disk or USB) under a unique file name.
In QBASIC, two main types of files exist:
Program File
A file that contains QBASIC instructions (source code) used for data processing.
Data File
A file that stores raw information such as name, address, marks, roll number, etc.
Example of a data file record:

File handling helps us to:
- Create a data file
- Store (write) data into a file
- Read data from a file
QBASIC supports two types of file access:
Sequential Access (one record after another)
Random Access (jump to any record directly)
In this lesson, we focus on Sequential File Handling.
2. Basic File Operations
A QBASIC program works with files using three main steps:
- OPEN a file
- READ / WRITE data
- CLOSE the file
3. Opening a File
Before reading or writing, you must open the file.
Syntax

Modes
ModeMeaningPurposeOUTPUTWrite onlyCreates a new file and writes from beginningINPUTRead onlyReads existing dataAPPENDAdd dataAdds new records at the end of an existing file
What happens when the file exists or does not exist?
ModeIf file existsIf file doesn't existOUTPUTOverwrites old fileCreates a new fileINPUTOpens fileError: File not foundAPPENDOpens fileCreates a new file
Examples

Alternative Syntax
4. Writing Data into a File
Steps to store data:
- Open file in OUTPUT (new file) or APPEND (add to existing file)
- Take inputs from user
- Store data using WRITE # or PRINT #
- Repeat if needed
- Close the file
WRITE # Statement
Adds commas between fields and puts quotes around strings.

Example

PRINT # Statement
Adds spaces between fields, no quotes around strings.
Syntax

5. Closing a File
A file must be closed after reading or writing.
Syntax

6. Reading Data From a File
Steps:
- Open file in INPUT mode
- Read each record using INPUT # or LINE INPUT #
- Display data
- Close file
INPUT # Statement
Syntax

Example

The number and types of variables must match the data stored.
LINE INPUT # Statement
Reads an entire line as one string.
Syntax

Reading All Records: The EOF Function
EOF(file number) checks if the end of file is reached.
Used like:

7. File Management Commands
These commands work outside programs (often in Immediate Window).
CommandPurposeFILESShows list of filesCHDIRChange directoryMKDIRCreate directoryRMDIRRemove empty directoryNAME…ASRename file or folderKILLDelete a fileSHELLExecute DOS commandsSYSTEMExit QBASIC
8. Programs for Practice
You already gave dozens, so here is a summary of what types you should know:
- Store single record
Store multiple records
Append records
Read all records
Read fixed number of records
Use LINE INPUT to read entire lines
Copy data from one file to another
Update records using temporary files
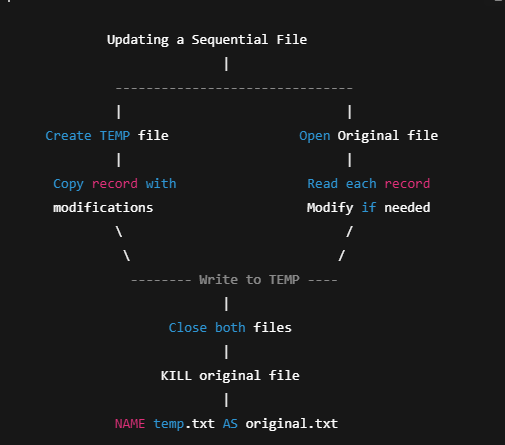
9. Updating Data Files in QBASIC
- QBASIC cannot edit records directly.
- Steps to update:
- Open existing file in INPUT
- Open a temporary file in OUTPUT
- Read each record
- Modify the record
- Write modified record to temp file
- Close files
- Delete original file using KILL
- Rename temp file using NAME … AS
10. Summary (Exam Friendly)
- File Handling lets us read/write data stored on disk.
- Files are opened using: OUTPUT, INPUT, APPEND.
- Use WRITE # or PRINT # to store data.
- Use INPUT # or LINE INPUT # to read data.
- Use EOF to detect end of file.
- Always close files using CLOSE.
- File management commands include: FILES, MKDIR, CHDIR, RMDIR, NAME AS, KILL, SHELL, SYSTEM.
Gallery

What is a File?
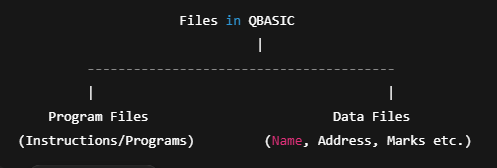
Types of Files in QBASIC
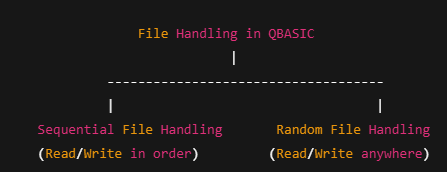
Types of File Handling in QBASIC
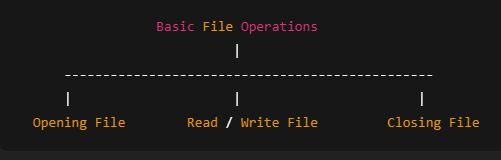
Basic File Operations Diagram
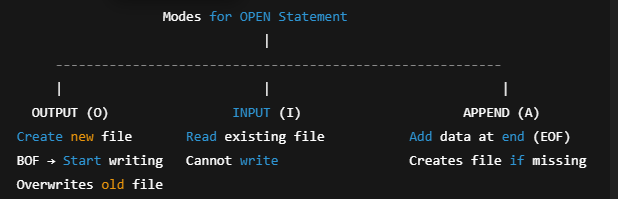
Modes of Opening Sequential Files
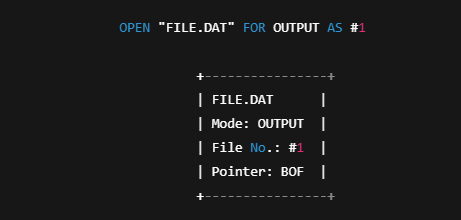
What Happens When You Open a File

Writing Data into a File (PRINT # / WRITE #)

Reading Data From a File (INPUT #)
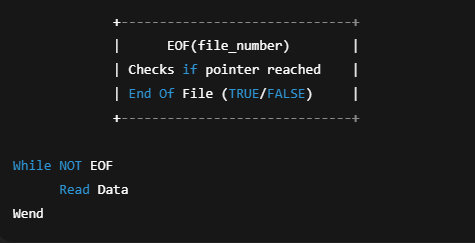
EOF Function Diagram

Complete Sequential File Handling Flowchart

File Management Commands Diagram