Number System
1. Evolution & Introduction
Early counting methods: fingers, sticks, stones, knots.
Development of symbols → systematic number systems.
Modern usage: Different systems for different fields (daily life, computing, engineering).
2. What is a Number System?
A set of symbols and rules used to represent numbers and perform arithmetic.
Base/Radix: Total number of distinct digits used.
Example: Decimal base = 10 → digits 0–9.
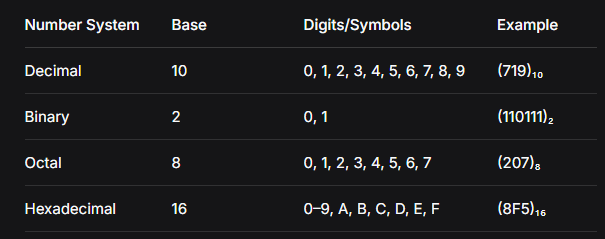
3. Types of Number Systems

🔢 Decimal System (Base 10)
Digits: 0–9.
Place values: Units (10⁰), Tens (10¹), Hundreds (10²), etc.
Example:
- (719)10=7×102+1×101+9×100(719)10=7×102+1×101+9×100
🔢 Binary System (Base 2)
Digits: 0, 1.
Used by computers (on/off states, transistors).
Example:
= 32 + 16 + 0 + 4 + 2 + 1 = (55)₁₀
🔢 Octal System (Base 8)
Digits: 0–7.
Used in computing (shorter than binary).
Example:
🔢 Hexadecimal System (Base 16)
Digits: 0–9, A(10), B(11), C(12), D(13), E(14), F(15).
Widely used in programming, memory addressing, color codes.
Example:
4. Binary Arithmetic (Deep Explanation)
4.1 Binary Addition
Rules:
0 + 0 = 0
0 + 1 = 1
1 + 0 = 1
1 + 1 = 0 carry 1 (i.e., 10 in binary)
Example:
1 1 1 0 1 (29 in decimal)
+ 1 0 1 1 (11 in decimal)
------------
1 0 1 0 0 0 (40 in decimal)
Carry explained:
Column from right:
1 + 1 = 0, carry 1
0 + 1 + carry 1 = 0, carry 1
1 + 0 + carry 1 = 0, carry 1
1 + 1 + carry 1 = 1, carry 1
1 + carry 1 = 10
4.2 Binary Subtraction
Rules:
0 – 0 = 0
1 – 0 = 1
1 – 1 = 0
0 – 1 = 1 borrow 1 from left column
Example:
1 0 1 1 0 (22 in decimal)
- 1 0 1 1 (11 in decimal)
------------
0 1 1 0 1 (13 in decimal)
In column 2 (from right): 0 − 1 → borrow from column 3, becomes 10 − 1 = 1.
4.3 Binary Multiplication
Rules: Same as decimal, but simpler:
0 × 0 = 0
0 × 1 = 0
1 × 0 = 0
1 × 1 = 1
Example:
1 0 1 (5)
× 1 1 0 (6)
--------
0 0 0
1 0 1
+ 1 0 1
-----------
1 1 1 1 0 (30)
14.4 Binary Division
Process: Similar to long division in decimal.
Example: (1101)₂ ÷ (10)₂
1 1 0 (quotient = 6 in decimal)
--------
10 | 1 1 0 1
- 1 0
-----
1 0
- 1 0
-----
0 1 (remainder = 1)
Result: Quotient = 110₂ (6), Remainder = 1.
5. Number System Conversions
5.1 Decimal to Other Bases
General Rule: Repeated division by the target base.
Decimal → Binary
Divide by 2, note remainder.
Repeat until quotient is 0.
Write remainders bottom to top.
Example: (46)₁₀ → (?)₂
(46)₁₀ → (?)₂
46 ÷ 2 = 23 rem 0
23 ÷ 2 = 11 rem 1
11 ÷ 2 = 5 rem 1
5 ÷ 2 = 2 rem 1
2 ÷ 2 = 1 rem 0
1 ÷ 2 = 0 rem 1
Read ↑ = 101110₂
(46)₁₀ = (101110)₂
Decimal → Octal
Divide by 8, note remainder.
Example: (345)₁₀ → (?)₈
(345)₁₀ → (?)₈
345 ÷ 8 = 43 rem 1
43 ÷ 8 = 5 rem 3
5 ÷ 8 = 0 rem 5
Read ↑ = 531₈
Decimal → Hexadecimal: Divide by 16, note remainder.
(255)₁₀ → (?)₁₆
255 ÷ 16 = 15 rem F
15 ÷ 16 = 0 rem F
Read ↑ = FF₁₆
5.2 Binary/Octal/Hex → Decimal
Method: Expand using place values (powers of base).
Binary → Decimal:
(1011)₂ = 1×2³ + 0×2² + 1×2¹ + 1×2⁰
= 8 + 0 + 2 + 1 = 11₁₀
Octal → Decimal:
(157)₈ = 1×8² + 5×8¹ + 7×8⁰
= 64 + 40 + 7 = 111₁₀
Hex → Decimal:
(1A3)₁₆ = 1×16² + 10×16¹ + 3×16⁰
= 256 + 160 + 3 = 419₁₀
Binary ↔ Octal
Binary → Octal: Group binary digits into 3 from right, convert each to octal.
(101110)₂ → 101 | 110 → 5 | 6 → (56)₈
Octal → Binary: Convert each octal digit to 3 binary digits.
(F3)₁₆ → F=1111, 3=0011 → (11110011)₂
octal ↔ Hexadecimal (via Binary)
Convert octal → binary → hex (or reverse).
Example: (345)₈ → binary → hex:
3=011, 4=100, 5=101 → (011100101)₂
Group 4: 0001 1100 1010? (pad leading zeros)
Actually: 011100101 → 0|1110|0101 → 0 E 5 → (E5)₁₆
6. Why Conversions Matter
- Computers use binary (0s and 1s).
- Humans use decimal.
- Octal and hexadecimal are shorter forms of binary used in programming, networking (IP addresses), digital circuits, cryptography, etc.
- Conversions allow communication between humans and machines.
7. Memory Aid & Tips
Base Values: B2 O8 D10 H16 (Binary 2, Octal 8, Decimal 10, Hex 16).
Hex Letters: A=10, B=11, C=12, D=13, E=14, F=15.
Binary Groups: Octal → 3 bits, Hex → 4 bits.
Conversion Flowchart:
Decimal ←→ Binary ←→ Octal
↓
Hex
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Forgetting to write base subscript: (101)₂ not just 101.
In binary addition: 1 + 1 = 0 carry 1, not 2.
In conversions: Group binary from right to left for octal/hex.
Hex letters A–F are case-insensitive but often written uppercase.
Gallery
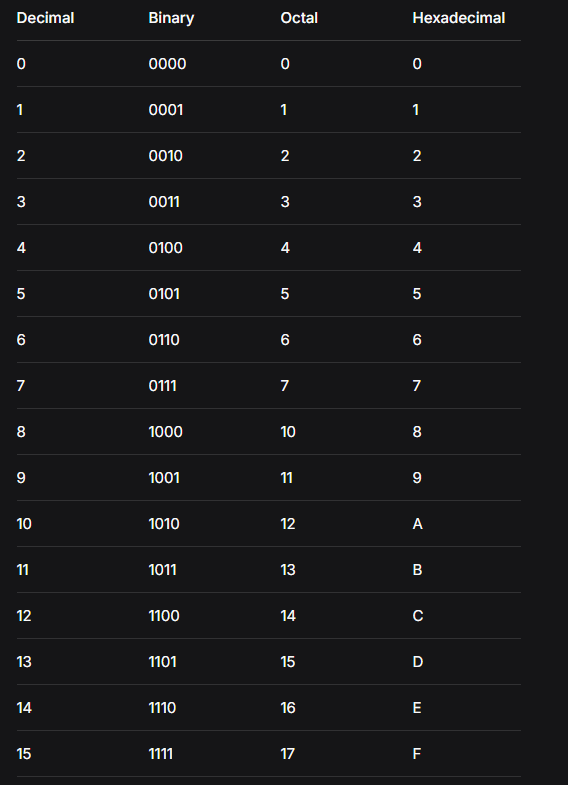
Conversion Table