1. Introduction to Programming
A computer is a fast, accurate machine, but it can’t think. It waits for humans to give step-by-step instructions. These instructions are called a program, and the person who writes them is a programmer.
A set of programs that helps a computer work is called software. To write programs, we use special languages called programming languages. Just like humans use Nepali or English to talk, computers use languages like C, Java or Python.
2. Types of Programming Languages
a) Machine Language
The oldest, most basic language.
Written using 0s and 1s.
Fastest for the computer but painfully difficult for humans.
b) Assembly Language
Uses short words called mnemonics (e.g., MOV, ADD).
Easier than machine language but still low-level.
Needs an assembler.
c) High-Level Language
Looks more like English.
Easy to write and understand.
Examples: C, Java, Python.
Needs translation:
Compiler
Interpreter
3. Approaches to Programming
To solve problems using a computer, programmers follow some methods.
i. Unstructured Programming
Everything is written in one long program.
Uses many jumps (GOTO statements).
Hard to understand, maintain or debug.
ii. Structured Programming
This is the hero of the chapter.
It breaks the problem into smaller parts called modules.
Features
Top-down approach
Uses three main structures:
Sequence (step-by-step)
Selection (if-else)
Loop (repeat until condition is met)
Makes programs easy to read, test and update.
Advantages
Less errors
Easier to understand
Easier to reuse parts
Good for team programming
4. Levels of Programming Languages
Programming languages are divided into levels:
a) Lower-Level Languages
Machine and Assembly language
Fast but hard for humans
b) Middle-Level Languages
Provide some low-level control but easier than assembly
Example: C language
c) High-Level Languages
Easy to read and write
Example: Python, Java, C++
5. Introduction to C Language
C is a high-level programming language created by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Laboratories in 1972.
Why is C so popular?
Fast and powerful
Can access memory and hardware
Used to build operating systems
Portable (runs on many computers)
Structured (supports modular programming)
Where is C used today?
Operating systems (like UNIX parts)
Compilers
Device drivers
Embedded systems
Scientific and engineering applications
6. Features of C Language
Simple
Fast execution
Portable (runs on many computers)
Structured language
Middle-level language
Rich set of operators
Extensible (allows user-defined functions)
Efficient memory management
7. Structure of a C Program
A C program always follows a specific pattern.

Parts of a C Program
1. Header files
Tell the compiler what libraries you want to use.
#include <stdio.h>
2. main() function
Where the program starts running.
3. Variables
Containers to store data.
4. Statements
Commands that the computer executes.
5. Braces { }
Define the beginning and end of blocks.
8. Data Types in C
To store different kinds of data, C uses data types.
Data TypeSizeExampleint2 or 4 bytes4, 100, -5float4 bytes2.5, 9.81double8 bytes3.1415926char1 byte'A', 'b'9. Variables and Constants
Variables
Names used to store values that can change.
Example:
int age = 18;
Rules for naming variables
Start with letter or underscore
No spaces
No special symbols
Case-sensitive
Constants
Values that do not change.
Example:
const float PI = 3.14;
10. Operators in C
Operators perform calculations.
a) Arithmetic
+, -, *, /, %
b) Relational
==, !=, >, <, >=, <=
c) Logical
&&, ||, !
d) Assignment
=, +=, -=, *=
11. Input and Output in C
Output: printf()
Used to display data.
Example:
printf("Hello World");
Input: scanf()
Used to get user input.
Example:
scanf("%d", &age);
Format Specifiers
TypeSpecifierint%dfloat%fdouble%lfchar%c12. Compilation Process in C
Steps from writing to running:
Editing
– Write the program
Compiling
– Convert C code into machine code
Linking
– Link library files
Execution
– Run the final output program
13. Basic Example Program

14. Applications of C Language
C is used in:
Operating system development
Database systems
Network drivers
Embedded microcontroller programs
Compilers and interpreters
Robotics
Game engines
15. Limitations of C Language
Even superheroes have weaknesses.
No built-in graphics support
No object-oriented features
No automatic garbage collection
Harder for beginners to master pointers
16. Why Students Should Learn C
Builds strong foundation
Helps understand how computers work internally
Useful for advanced languages like C++, Java, Python
Almost every engineering and CS course starts with C
Gallery
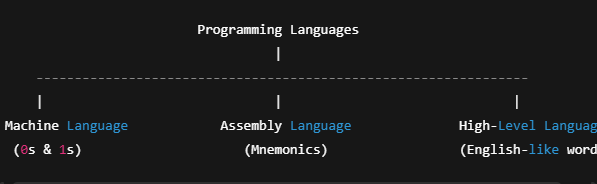
Types of Programming Languages

Approaches to Programming
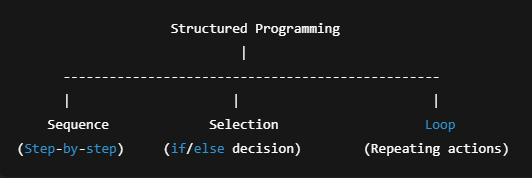
Structured Programming Flow

Top-Down Design

Levels of Programming Languages
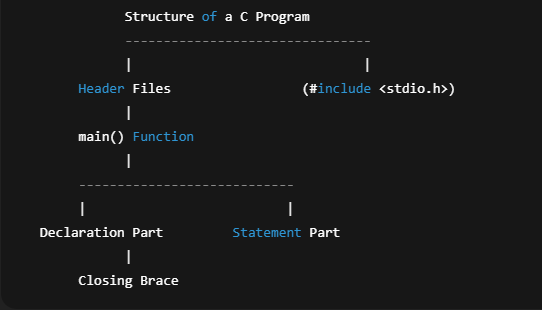
Structure of a C Program

Compilation Process in C
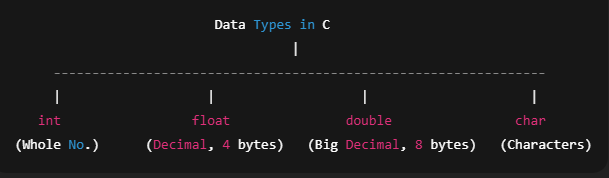
Data Types in C
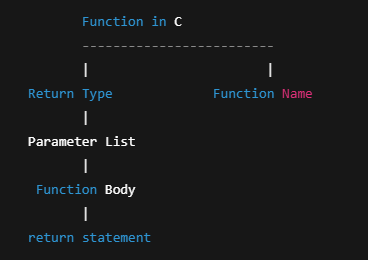
Structure of a Function in C
